Introduction
Large strongyles
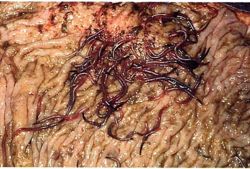
The common large strongyle species infecting equids are Strongylus vulgaris, S.edentatus and S. equinus. Similar species are observed in horses and donkeys. A new species, Strongylus asini, has been seen in donkeys and other wild equids. Triodontophorus spp., some Craterostomum spp., and Oesophagodontus robustus are also in this group.
- S. vulgaris are pathogenic due to damage caused by vascular migration
- A study in Zimbabwe has shown that the intensities of infection of adults in the large intestine and larvae in the cranial mesenteric artery and its branches were much higher than those recorded in horses (Pandey and Eysker, 1989)
- S. edentatus migrates through the liver and peritoneum, causing associated damage
Similar pathogenic effects of S. vulgaris in donkeys to those found in horses have been reported. In donkeys, various lesion types have been recorded. These include minimal arterial lesions, small thrombi and substantial thrombi, the size of a tennis ball, where the arterial wall is greatly thickened, corrugated, gritty and full of larvae. These arterial lesions, which can interfere with the blood supply to major parts of the alimentary tract, may be one of the major contributory factors for the weakness, low productivity and early demise of working donkeys.
Small strongyles – Cyathostomins
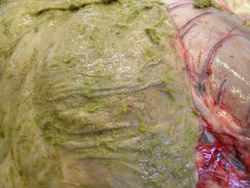

Cyathostomins were formerly called trichonemes or cyathostomes. Adult worms live in the large intestine and have a non-migratory life cycle. Infections with these nematodes typically include very large populations and numerous species. Over 50 species of cyathostomins have been recorded in horses, donkeys and zebras (Lichtenfels et al, 1998). The species of cyathostomins described in donkeys are similar to those described in horses, but ten species were found to be specific to donkeys and zebras.
Until recently, the more obvious lesions caused by Strongylus vulgaris, as well as the frequent finding of large burdens of cyathostomins in apparently healthy animals, resulted in a perception that cyathostomins were not pathogenic. After a marked decrease in the prevalence of S. vulgaris in particular, there has been an increasing number of reports of serious intestinal diseases attributed to cyathostomins in horses. They are now considered one of the major causes of colic in equines in most regions of the developed world.
The main features of this group are as follows:
- Adult cyathostomins produce typical strongyle eggs indistinguishable from large strongyle eggs
- Eggs excreted in faeces hatch in favourable conditions to third stage larvae (L3)
- L3 larvae are resistant to desiccation and harsh climatic conditions
- Ingested L3 larvae do not penetrate deep tissues but undergo development in the tissue of the large intestine
- The larvae are able to go into a dormant or hypobiotic state and encyst in the epithelial cells of the large intestine
- The encysted larvae are fairly resistant to anthelmintics including ivermectin. Moxidectin (Fort Dodge claims that 80% of encysted developing larvae of small strongyles are eliminated) is effective against some of the developing encysted larvae
- The mechanism that triggers the larvae to enter or come out of hypobiosis has not yet been fully investigated, but may be associated with the elimination of adults in the gut following anthelmintic treatment
Acute verminous enteritis (larval cyathostomosis)
This occurs in late winter or early spring as larvae emerge in large numbers simultaneously.
Diagnosis
The objective of a worm control programme is to prevent signs of helminthosis, the clinical disease associated with helminths. Diagnosis of helminthosis can be based on:
History
- Suggesting poor management and lack of an effective anthelmintic programme
Clinical signs
- Diarrhoea
- Colic
- Ill thrift
- Weight loss
Acute verminous enteritis (larval cyathostomosis)
- Initially symptoms of abdominal pain, anorexia and depression are presented and hyperlipaemia quickly follows
- Severe inflammation with sub-mucosal oedema and haemorrhage in the caecum and colon may result in severe diarrhoea but, in the donkey, death due to ‘toxic shock’ may occur before diarrhoea develops
A second form of this larval cyathostomosis has been reported in the horse:
- Diarrhoea is not a feature
- Signs of ill thrift and weight loss are seen
- It occurs in the grazing season
- The progressive accumulation of hypobiotic larvae causes thickened intestinal mucosa
- Thickened mucosa leads to poor intestinal absorption of nutrients
Laboratory tests

- Faecal examination for eggs or larvae
Identification of the eggs in the faeces does not, however, indicate the presence of a clinical disease, and only when large numbers of eggs per gram (epg) have been identified can the possibility of clinical disease be considered. Conversely, as the disease may be caused by the larval stages of the parasites (as is the case with cyathostomins), then the epg may be within normal limits whilst resultant disease is present.
- Haematology: red blood cell count, serum protein level
Both forms of acute verminous enteritis (larval cyathostomosis) may be difficult to diagnose ante-mortem from faeces, as the donkeys affected are often on anthelmintics, which will control egg-shedding by adult worms. The parasite may also still be in its prepatent period. Less than 1% of donkeys at The Donkey Sanctuary have evidence of encysted larvae at post-mortem. At post-mortem the mucosa of the caecum and colon is congested with gross oedema of the sub-mucosa. Ruptured cysts are numerous.
Treatment
Anthelmintics used prophylactically and to treat acute and chronic worm infections can be categorised into four main groups as shown below.
Ivermectin can effectively control adult and migrating larvae of large strongyles. As a result, colic due to thrombo-emboli caused by S.vulgaris in the vasculature of the caecum and ventral colon and damage by other large strongyle larval migration are less common in the UK. The threat from helminths has shifted away from large strongyles to small strongyles, the cyathostomins.
In any donkey population treated with ivermectin it is possible to eradicate large strongyles if it is given on a regular basis for long enough and combined with pasture management. Cyathostomins are more difficult and require secondary measures, as do certain other endoparasites, including Strongyloides westeri, or Parascaris equorum in foals, and tapeworms.
The Donkey Sanctuary uses combination of fenbendazole, prednisolone and ivermectin to treat suspected cyathostomosis. Supportive treatment for hyperlipaemia may also be needed.
Anthelmintic drugs used in the donkey
Control
The anthelmintic control programme which has been operating at The Donkey Sanctuary for many years now has been devised so that it fulfils the following criteria:
- it is effective in controlling helminths
- it reduces the incidence of cyathostomosis
- it slows down the development of resistance to anthelmintics
- it is cost-effective. The reduced cost of anthelmintics has offset the increased laboratory costs.
At The Donkey Sanctuary no donkey is given anthelmintic unless it has a positive egg count above 200 epg. Although this effectively means regularly examining the faeces of all the donkeys, it has several beneficial effects:
- To reduce handling and stress to the donkey when the whole herd is wormed
- To reduce exposure of adult worms to repeated doses of anthelmintic and therefore development of resistance
- To help create a ‘refuge’ of susceptible larvae on the pasture to compete with resistant strains
Trawford et al (2001) showed that moxidectin suppresses faecal egg output for longer than ivermectin in the donkey. It was not established whether this is due to the effect against encysted cyathostomin larvae or due to the longer presence and higher concentration in the blood compared to ivermectin. The greater effect of moxidectin against encysted larvae has led to its preferential use over ivermectin but the worm control programme is under constant review.
It is claimed that 99% of worms occur on the pasture, whereas 1% occur in the horse (Rose et al, 2000). This statement is equally applicable to the donkey and so no worm control programme should depend solely on drugs. It should also include good pasture and stable management:
- Good stable hygiene
- Rotational grazing, proper pasture management and harrowing pastures is most important
- The use of a ‘biological vacuum’ (sheep3 ) is still pertinent to ingest larvae on the pasture and is used on the Donkey Sanctuary’s land both in winter and early spring.
- Removal of dung at least twice a week in the summer is carried out mechanically
- If donkeys are at pasture in the winter months then faecal sampling may need to be carried out throughout the year
- Grazing pasture should be rested at least five months of the year (the estimated survival time of cyathostomins)
- Managing young stock, which has lower worm larva immunity, on separate pastures from older groups
3 The use of sheep may increase the incidence of the stomach worm Trichostrongylus axei, but the pathogenecity of this species in donkeys is rarely a problem.
Application of the above principles can be applied to donkeys in most cases. Owners should always be advised to consult their veterinary surgeon regarding periodicity of faecal sampling/worming with regard to their own specific circumstances.
Under tropical weather conditions in most developing countries, the dry season is not favourable for the development and survival of the freeliving and parasitic stages and so there is relatively little danger of acquiring infection at this time of year. Generally, animals have a high probability of acquiring infection from pasture during and immediately following wet seasons. Treating donkeys at the beginning and end of the rainy season therefore seems to be sufficient under such climatic conditions. This is usually practised in Ethiopia and other developing countries where the farmers cannot afford frequent treatment for their animals.
The efficacy of worming strategies in any country should be carefully monitored by laboratory analysis and condition scoring. An epidemiological assessment of weight loss or anaemia should complement any monitoring process to determine the impact of dental disease and/or poor nutrition.
References
- Trawford, A. and Getachew, M. (2008) Parasites In Svendsen, E.D., Duncan, J. and Hadrill, D. (2008) The Professional Handbook of the Donkey, 4th edition, Whittet Books, Chapter 6
- Lichtenfels, J.R., Kharchenko, V.A., Krecek, R.C., and Gibbons, L.M. (1998). ‘An annotated checklist by genus and species of 93 species level names for 51 recognised species of small strongyles (Nematoda: Strongyloidea: Cyathostominea) of horses, asses and zebras of the world’. Vet. Parasitol., 79. pp 65-79.
- Pandey, V.S., Eysker, M. (1989). ‘Strongylus vulgaris in donkeys (Equus asinus) from the highveld of Zimbabwe’. Vet. Parasitol'. 32. pp 173-179.
- Rose, R.J., Hodgson, D.R. (2000). Manual of Equine Practice. W.B Saunders, Pennsylvania, USA.
- Trawford, A.F., Morriss, C.J., Bell, N.J., and Reid, S.W.J. (2001). ‘Comparing the Efficacy of Moxidectin with Ivermectin in the Donkey’. Paper presented at: The 18th International Conference of the World Association for the Advancement of Veterinary Parasitology. 26-30 August. Stressa, Italy.
|
|
This section was sponsored and content provided by THE DONKEY SANCTUARY |
|---|