Toxoplasma gondii
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
- Major pathogenic species called Toxoplasma gondii
- Causes disease in a wide range of animal species including humans
- Important cause of abortion in sheep
- Zoonotic
- Can cause abortion
- Can cause congenitally aquired defects
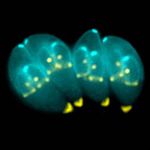
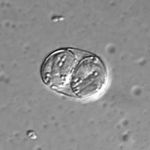
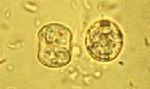
- Forms a sporulated oocyst which is only 10μm
- Contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites
- Transmission through ingesting the intermediate host or via the faecal-oral route
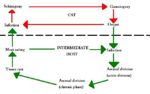
Life Cycle
- Complex
- Usually indirect
- Referred to as facultatively heteroxenous
- Intermediate host is not essential for completion of the life cycle
- Gametogony (sexual stage) is host specific for felids
- Any warm blooded animal can act as a facultative intermediate host
- Asexual reproduction occurs in the intermediate host forming tissue cysts
- Intermediate host swallows sporulated oocysts or tissue cysts
- Can be transferred between intermediate hosts by carnivorism
- Cats
- Sporulation occurs in 2-3 days
- Cats either swallow infective (sporulated) oocysts where Toxoplasma gondii has a prepatent period of 3 weeks
- Or eat the tissues of an infected intermediate host where Toxoplasma gondii has a prepatent period of 3-10 days
- Self-limiting infection
- Oocysts are shed for 1-2 weeks
- Shedding can occur later if immunity wanes or cat is immuno-compromised
- Intermediate host
- 3 sources of infection
- Oocysts from environment contaminated by cat faeces
- Eating cysts in tissues of other infected hosts through carnivorism or undercooked meat
- Transplacental transmission in some host species during the acute phase of infection
- 3 sources of infection
- Acute phase of infection
- After infection of the intermediate host the organism undergoes a phase of rapid division and dissemination throughout the body
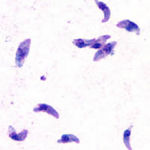
- Parasite enters cell and asexual reproduction occurs by endodyogeny (budding) producing 8-16 tachyzoites
- Tachyzoites are released when host cell bursts
- Haematogenous spread as more cells are infected
- Infection continues until the animal develops immunity (around 2 weeks) at which point the infection enters the chronic phase
- After infection of the intermediate host the organism undergoes a phase of rapid division and dissemination throughout the body
- Chronic phase of infection
- Occurs once the host's immune response has become effective
- Groups of slow growing intracellular bradyzoites become walled off forming infective cysts
- Bradyzoites inside cysts are protected from the host immune response whereas extracellular tachyzoites are killed
- Cysts remain viable for months to years and are particularly numerous in muscle and nervous tissue
- If immunity is suppressed the infection can revert to the acute form
- Occurs once the host's immune response has become effective
- Meat animals
- Significant proportion of cattle, sheep, pigs and rabbits can tissue cysts
Pathogenesis
- Cattle and horses
- Sometimes infectious causing opthalmitis
- Dogs
- Complication of canine distemper
- Causes pneumonia and encephalitis
- Toxoplasma can cause acute interstitial pancreatitis in systemic toxoplasmosis
- Toxoplasma gondii causes myositis
- Cats as final hosts
- Intermediate hosts, birds and mammals have tachyzoites throughout body, infrequently in skeletal muscle
- Histologically:
- Multifocal necrosis of myofibres
- Lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltration
- In later stages bradyzoite cysts
There is abortion late in gestation following infection with oocysts from cat faeces. Ewes are not clinically ill and the foetus has no gross lesions. Characteristically the cotyledons are bright red with multiple (1-3 mm) white/yellow foci (strawberry cotyledons).