Thrombosis may be due to:
- Endothelial injury.
- Altered blood flow E.g. abnormal stasis.
- Hypercoagulability.
Often associated with other disease processes for example Disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Commonly see posterior paralysis of cats with cardiomyopathy.
Spontaneous venous thrombosis is rare. Seen in cattle with traumatic reticulo-peritonitis in the caudal vena cava.
Description
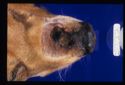
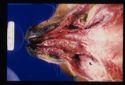
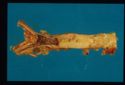
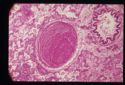
Thrombosis is a localized or generalized intravascular clot formation. Thrombi form as the result of trauma or pathological processes affecting the blood vessel endothelium or disturbances to blood flow and/or blood composition. Some diseases such as infective endocarditis and heart worm increase the risk of thrombi formation.
Diagnosis
History & Clinical Signs
- Signs depend on the area affected and the size of the blocked vessel.
- Poor perfusion below affected area.
- Malfunction and necrosis of affected organs
Laboratory Findings
Abnormalities associated with lack of blood perfusion and/or pathological conditions.
Ultrasonography
- Blood stasis
- Visualization of a thrombus
Angiography
- May show lack of opacity in affected region
Treatment
-Treat underlying problem
-IV Fluids
-Anticoagulant (Heparin for short term treatment, Aspirin for long term treatment)
Prognosis
-Depends on underlying condition