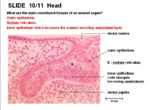
Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology
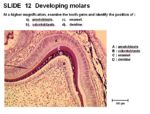
Anatomy of the Enamel Organ
The main components which form the enamel organ are:
- Outer epithelium
- Stellate reticulum- star shaped cells lying between the outer and inner epithelial layers. It has the appearance of connective tissue but is of epithelial derivation.
- Inner epithelium which becomes the enamel secreting ameloblast layer
The enamel organ has many different components. These consist of:
Crown
The crown is covered by enamel. It meets the root at the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ).
The crown of incisors have only one cusp. The crown of molars have up to 4 cusps for the grinding of food.
Root
Teeth may have one or more roots. The furcation angle is the point where roots diverge. The root ends in an apex which is where the nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics travel to the pulp. Hypsodont teeth can have open roots (aradicular) e.g. in rabbits which have continued growth. Hypsodont teeth can have closed roots (radicular) e.g. horse where growth decreases with age. Brachydont teeth have no capacity for growth and so the roots are closed.
Species Differences
The apex has a single foramen in dogs and cats. It remains open in herbivores. In the horse, the apex closes as the animal ages. Brachiocephalic dogs often have fused roots. Equine incisors have fused roots. In the horse's canines, the size of the root is much larger than the crown.
Alveolar Bone
The alveolar processes of the jaw consists of the alveolar bone, trabecular bone and compact bone.
The densest bone called the cribiform plate lines the alveolus. This appears white on radiographs and is referred to as the lamina dura.
Lamina Dura
The lamina dura lines the alveolar bone. If uninterrupted, it indicates good dental health.
The lamina dura is seen as a white line radiographically.
Enamel
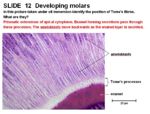
Enamel has an ectodermal origin. It is synthesised by ameloblasts. It is very hard, densly calcified and acellular, therefore cannot regenerate.
Complicated enamel folding occurs in teeth where the crowns are high. Enamel forming secretions pass through processes of apical cytoplasmic extension called Thomes' Fibres.
Dentine
Dentine is a calcified, collagen rich matrix. It is synthesised by odontoblasts.
Secondary dentine is produced throughout life and increases with rate of repair. It is darker in colour than primary dentine.
Cementum
Cementum is synthesised by cementoblasts. It is calcified tissue and lacks regular organisation. Collagen fibres extend from the cementum into the periodontal ligament to fasten the tooth in its socket. Cementum is relatively immune to pressure erosion, therefore the tooth can be be romedelled in its socket.
Pulp
Pulp fills the dental cavity. It is a delicate connective tissue bordering the odontoblast layer. It is highly vascularised and contains a lymphatic plexus.
Pulp allows pain sensation to thermal, mechanical and chemical stimulants. Most of the nervous supply is sensory, with some vasomotor input.
Periodontal Ligament
The collagen fibre bundles are called Sharpey's fibres. The fibres insert into the alveolar bone and cementum of the tooth.
There are 3 categories: gingival, trans-septal and alveolodental. There are evenly distributed blood vessels and nerve fibres transmitting thermal, pain and pressure sensation. Some species can also sense proprioception in the periodontal ligament.
The main cells of the enamel organ are: