Oesophagus - Anatomy & Physiology
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
BACK TO ALIMENTARY - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
Introduction
The oesophagus (or gullet) is a muscular tube which transports food from the pharynx to the stomach. A bolus of food is passed down the oesophagus by peristalsis.
The oesophagus is divided into cevical, thoracic and abdominal sections.
Structure and Function
- Begins dorsal to cricoid cartilage of larynx
- Follows trachea down neck, first on the left and then medially once in thorax in the mediastinum
- Passes over heart then through the oesophageal hiatus of the diaphragm
- Passes over the dorsal border of the liver then joins the stomach at the cardia
- The cervical section is accompanied by the common carotid artery, the vagosympathetic trunk and the recurrent laryngeal nerves
- The thoracic section is accompanied by the right and left vagus nerves (CN X)
- Different proportions of striated muscle across the species
-Dog and ruminant = 100% -Cat = 80% (rostral) -Horse = 65% (rostral) -Pig = 33% (rostral)
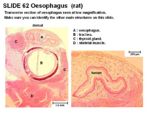
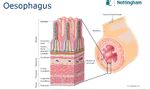
Histology
- Stratified squamous epithelium
- Mucosal folds for distension
- Degree of keratinisation depend on diet
- Lamina propria contains collagen and elastic fibres sparsely distributed
- Lamina muscularis is smooth muscle
- No glands in mucosa
- Mucous glands (tubulo-acinar) present in submucosa
- Inner circular layer of tunica muscularis thickens near gastric junction forming a sphincter
Innervation
- Sympathetic nerves
- Parasympathetic from the vagus nerve (CN X) and recurrent laryngeal nerves
- Myenteric plexus extends the length of the oesophagus
Species Differences
- Mucous glands present in horse, cats and ruminants only at pharyngeal-oesophageal junction
- Thick and strong sphincter of tunica muscularis in dogs and pigs
- Ruminants, horse and pig have stratified squamous epithelium continuing from oesophagus into stomach. carnivores have an abrupt transition to columnar epithelium.
Canine
- Canid has no keratinisation
- Lamina muscularis present caudally in dogs (spirally aranged)
- Lamina muscularis absent cranially in dogs
- Mucous glands throughout in dog but more abundant caudally
Equine
- Horse has some keratinisation
Ruminant
- Ruminant has a lot of keratinisation
Porcine
- Lamina muscularis present caudally in pigs (very thick)
- Lamina muscularis absent cranially in pigs
- Pig has some keratinisation
- Mucous glands abundant cranially but absent caudally in pig
Avian
- Avian differences- the crop
- Ducks have an oesophangeal tonsil present in the caudal segment of oesophagus