Mites
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
Astigmata Introduction
Mites are one of the most successful and diverse vertebrate groups. The species of veterinary importance are parasitic, although a few non-parasitic mites are also important, such as oribatid and forage mites.
Mites are very small, on average under 0.3mm in length and for this reason often go unnoticed. They spend the majority of their life cycle on the host and cause mange.
The body shows no segmentation but can be divided into two sections, the idiosoma and the gnathosoma. Adult and nymphs have four pairs of legs, whereas larvae have only three pairs of legs.
The taxonomy of mites is complex as there are over 8 families. In this article the families are split according to their location on the host into sub-surface (burrowing) and surface (non-burrowing) mites.
Burrowing Mites
Sarcoptidae
Sarcoptes
Recognition
- Small, round mite
- Short legs
- Project only a short distance from body margin
- Dorsal spines
- Arranged in rows
- Terminal anus
- Male is about 250μm in length and the female about 400-430μm in length
Life Cycle
- 3 weeks life cycle
- Female lays eggs in epidermis in an egg laying pocket
- Female feeds on liquid oozing from damaged tissue
- The eggs hatch in 1 week
- 6 legged larvae released which crawl to skin surface
- The larvae then burrow back into the epidermis into moulting pockets
- Larvae moult to become 8 legged nymphs
- Nymphs moult twice before becoming adults
- Adult males emerge and look for females to mate
Transmission
- Close contact
- Adults and larvae can be transferred from one skin surface to another
Pathogenesis
- Erythema with papule formation
- Scale and crust formation
- Alopecia
- Intense pruritis for one week
- Self-inflicted trauma
- Scab formation
- Wrinkling and thickening of skin
- Hypersensitivity may develop
- Rash develops
- Sarcoptes scabiei
- In scabies
- Strains of S. scabiei can be passed between different animals and cause clinical signs although the infection is likely to resolve spontaneously and be unlikely to establish
Diagnosis
- Skin scraping until capillary blood appears
- Adults, eggs, immature mites and faecal pellets can be seen microscopically
- Place material on a microscope slide
- Add 10% KOH
- Warm slide over bunsen flame
Treatment
- Acaricide
- For more information on acaricides click here
- Treat both infected and in-contact animals
- Older products have to be given in repeat treatments
- Avermectins are effective in farm animals
- Selamectin is available as a good spot-on for dogs
- Control for pigs:
- Treat sows before entering the farrowing pen
- Treat boars at 6 month intervals
Sarcoptic Mange
Dogs
- Highly contagious
- Intense pruritus
- First signs appear at edges of ears, then progresses to muzzle, face and elbows
Cats
- Rare
Pigs
- Important condition as 35% pigs are asymptomatic carriers
- First signs of infestation appear on the ears before spreading to the rest of the body
- Transmission from sow to piglets whilst suckling and from boars to gilts at service
- Infestation adversely affects productivity
Cattle
- Most frequently seen in housed cattle
- Notifiable in USA and Canada
- Often called 'neck and tail mange' as lesions most often seen on neck and tail
- Infestation adversely affects productivity
Sheep
- Notifiable in UK
- Lesions on hairy parts of face
- E.g. Face, ears, axillae and groin
- Causes considerable hide damage in local African breeds of long haired sheep
Horses
- Notifiable in UK
- Lesions begin on head, neck and shoulders then spread to rest of body
Knemidocoptes
- Only genus of burrowing mites which occurs on avian species
- Life cycle similar to Sarcoptes spp.
- Diagnosis based on clinical signs and discovery of mites
- Repeat treatments with acaricides needed
- Few products licensed for use in poultry
Recognition
- Small, round mite
- Short legs
- U-shaped chitinous bar behind head
- Terminal anus
- K. mutans
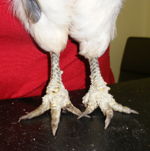
- Scaly leg in poultry
- Mites burrow beneath leg scales causing them to loosen and rise
- Ragged appearance to legs and feet
- Distorted claws and feet
- Infected birds are usually lame
- K. gallinae
- Depluming itch in poultry
- Burrow into feather shafts
- Intense pain and pruritus
- Birds pull out body feathers
- K. pilae
- Scaly face and beak in psittacines
- Mites attack bare or lightly feather areas of the face, beak, cere and body
- Scaliness at the base of the beak is the first sign which then spreads
- Little pruritus
Trixacarus
- Similar to Sarcoptes but half the size
- Causes severe pruritus in laboratory rodents
- Burrowing activity causes biting, scratching and irritation
- Leads to inflammation, pruritus and alopecia
- Affected areas show acanthosis and hyperkeratosis
- Death can occur within 3-4 months of infection
- Transmission is due to close contact between mother and offspring
Demodex
- Demodex spp. found on all domestic mammals and in humans
- Each host has its own species
- Causes demodecosis
Recognition
- Cigar shaped
- Four pairs of stumpy legs on the anterior end
- Long and narrow to fit into hair follicles
Life Cycle
- Live as commensal organisms
- Live in hair follicles and in sebaceous glands
- Life cycle takes 3 weeks
Pathogenesis and Epidemiology
- Initial infection is slight hair loss which may resolve spontaneously or could spread over the body
- Squamous demodecosis
- Less serious
- Dry reaction
- Alopecia, desquamation and skin thickening
- Absent to mild pruritus
- Follicular/pustular demodecosis
- More serious
- Skin invasion by Staphylococci
- Skin becomes wrinkled, thickened and contains pustules which ooze serum, blood or pus
- Affected animals may be seriously disfigured
- Severe pruritus is associated with secondary infection
- Immune factors are important in determining the severity and occurrence of demodecosis
- Familial susceptibility
- Immunosuppression
- Immunosuppressant therapy
Cats
- Rare
- Confined to the periocular region
- Mild squamous type only
Cattle
- Pea-sized nodules in the skin
- Each nodule contains several thousand mites
- Affects hide quality
- Economically important in Australia
Goats
- Becoming more common in goats
- Disease similar to that in cattle
Pigs, Sheep and Horses
- Rare
Diagnosis
- Liquid paraffin applied to a skin fold
- Deep skin scraping
Control
- Not easily accessible to acaricides due to their deep location in the skin
- Repeat treatments needed
- Recovery may take several months
- To aid acaricide penetration, clipping a dog's coat and washing is recommended
Notoedres
- Known as feline scabies
- Also common ectoparasites of tropical bats
- Parasite of cats, rats, man and rabbits
Recognition
- Similar to Sarcoptes
- Less distinct angles on body surface
- Females have suckers on legs one and two
- Females are about 225μm in length and males 150μm
- Anal opening is distinctly dorsal (not posterior)
Pathogenesis
- Infection begins on the ear tips and spreads over the body
- Notoedres cati in notoedric skin infestation
- Causes dermatitis
- Burrowing of females damages keratinocytes leading to cytokine release
- Hypersensitivity reaction may occur
Diagnosis
- Superficial skin scraping
- A single nest in a scraping may yield many mites
Non-Burrowing Mites
- Live on the skin surface
- Feed on either skin scales and tissue or suck blood
Psoroptes
Recognition
- Oval shaped
- Long legs
- Funnel shaped suckers on segmented pedicels
- 1-2mm in length
Life Cycle
- Confined to skin surface
- Feed on serous exudate by siphoning
- Adult female can lay up to 100 eggs during her life time (one month)
- 10 day life cycle
- 2 nymphal stages
Psoroptes cuniculi
- Parasite of rabbits
- Common among conventional rabbits
- Transmitted via contact
- Adapted to living in an aural environment
Pathogenesis
- The ears are painful and itch intensely
- Affected rabbits shake their heads and scratch their ears
- The inner surfaces of the pinnae are covered with brown, scaly, fetid material, and the skin beneath is raw
- Mites are grossly visible
- Histologically, there is chronic erosive and proliferative eosinophilic dermatitis
- The mites are non-burrowing and thus are found only in the exudate, not in the tissue
Diagnosis
- Microscopic examination for mites (low magnification)
- Appearance
Control
- Infestations are difficult to eliminate from a colony
- Ivermectin is usually effective
Psoroptes ovis
- Adult females are large mites at 750μm in length
- Males identified by copulatory suckers and paired posterior lobes
- Males attach to deutonymphs (second moult after larval stage) in a process called copula
- Males remain in copula until females moult for the last time
- Copulation occurs
- Life cycle last 14 days
- Transmitted by direct contact between sheep
- Indirect transmission can also occur
Pathogenesis
- Economically important ectoparasite of sheep
- Causes sheep scab
- Wool loss, restlessness, biting, scratching of infested area and decreased productivity through decreased weight gain
- Usually seen in late autumn and early winter (although may also occur in late summer)
- Population numbers decline after shearing due to a change in the microclimate, then build up again as the fleece grows
- Notifiable in UK
- Mites found under scabs and in skin folds
- Lesions most common on flanks, neck, back and shoulders
- Causes pruritic condition of cattle
- Active in keratin layer
- Mouthparts abrade the skin
- Antigenic material in mite faeces can lead to hypersensitivity reactions
Diagnosis
- Skin scraping
- KOH added
- Warm slide over a bunsen flame
- Examine under a microscope
Chorioptes bovis
- Surface parasite of horses and cattle
- Less pathogenic than Psoroptes
- Mouthparts cannot pierce the skin
- 3 week life cycle
Recognition
- Oval body
- Long legs
- Cup shaped suckers on unsegmented pedicels
- Females about 300μm in length
Pathogenesis
- Chorioptic mange
- Often seen in rough-legged horses with heavy feathering
- Induce crusty skin and lesions below the hocks and knees
- Mild condition in cattle
- Rubbing and scratching
- Hide damage
- Usually affects the base of the tail, perineum and udder
- Usually found on legs of sheep
- Mild condition
Otodectes cynotis
- Commonest mange of dogs and cats in the world
- Inhabits the inner ear
- Also found in the fox and the ferret
- Closed keratinous bars (apodemes) on ventral surface
- 3 week life cycle
- Feeds on ear debris
Pathogenesis
- Only a few cats show symptoms
- Transmission occurs whilst kittens are suckling
- Common cause of otitis externa in dogs
- Brown waxy exudate produced
- Can lead to secondary infection
- Clinical signs apparent
- Head shaking, ear scratching and aural haematomata
Treatment
- Acaracidal ear drops
- Massage base of ear to disperse drops after treatment
- Most treatments need to be repeated in 10-14 days to kill newly hatched mites
- Selamectin can be used as a spot-on treatment
- Prolonged duration of action
- Treat all in-contact animals
- These may be asymptomatic carriers
Cheyletiella sp.
- Surface mite of cats and dogs
- Also found on humans and rabbits
- C.yasguri (dogs), C.blakei (cats and humans) and C.parasitivorax (rabbits)
Recognition
- Waisted body
- Claw like palps on head
- Combs at ends of legs
Pathogenesis
- Highly contagious
- Mild pathogenesis
- Causes very scaly dermatitis
- Can be transferred to humans
Diagnosis
- Clinical signs
- E.g. Excess scurf
- Brush scurf onto dark paper
- 'Walking dandruff' as mites will move when present in large numbers
- Skin scrapings
- Hair pluckings from scaly areas
- Eggs may be present
Dermanyssus gallinae
- 'Red mite' of poultry
- Spends most of time off the host
- Adults and nymphs visit poultry at night to feed
- 1 week life cycle
- Adults can survive several months without feeding so reservoirs can build up
Appearance
- Spider like mite with long legs
- White or grey
- Becomes red when engorged with blood after feeding
- Few hairs on body
- Hooks on legs
Pathogenesis
- Blood sucking mite
- Lesions usually found on the breast and legs
- Irritation, restlessness, decrease in egg production
- Anaemia can result if mites are present in large numbers
- Newly hatched chicks can rapidly die if infested
Treatment
- Acaricide
- Environmental treatment
- Remove wild bird nests
Ornithonyssus
- Also called the 'Northern mite' or 'Northern feather mite'
- Closely related to Dermanyssus
- Hairy
- Spends entire life cycle on the host
- Occurs in caged birds and poultry
- Causes feathers to become matted and severe scabbing can develop
- Scabs particularly seen around the vent
- Decreases egg production
- Grey or black discolouration of feathers when large numbers of mites are present
Trombicula autumnalis
- Also called the 'harvest mite'
- Not host-specific
- Will parasitise any animal, including humans
- Only the larval stage is parasitic
- Nymphal and adult stages are free-living in the soil
- Mite numbers are highest in late summer in temperate climates
- Mite numbers are constant all year in tropical regions
Recognition
- Six legs
- Bright orange in colour
- Hairy
- No spiracles
- Breath through cuticle
Pathogenesis
- Larvae insert mouthparts into skin and inject cytolytic enzymes
- Feed on partly digested host tissue
- Causes irritation
- Can cause a hypersensitivity reaction
- Mites found on head, ears and flanks of pets
- Mites found on face and limbs of grazing animals (depending upon host height)
Control
- Very difficult
Treatment
- Fipronil spray applied to affected areas
Leporacarus
- Known as the 'rabbit fur mite'
- Found on rabbits (domestic and wild) and on hares
- Common
- Clings to individual hairs
- Feeds on sebaceous secretions and skin debris
- Non-pathogenic
- May cause dermatitis in humans handling infected animals
Forage Mites
- Pests of stored food products, hay and straw
- May cause skin reactions and respiratory/intestinal disturbances in animals and humans
- Control relies upon:
- Identifying and destroying infected feed and bedding
- Thoroughly cleaning feed storage bins
- Keeping feed storage areas clean and dry
Varroa destructor
- More commonly known as the 'honeybee mite'
- Notifiable disease in the UK
- Oval
- 1-1.5mm in length
- Eggs are laid in the hive and develop with the brood cells
Pathogenesis
- Blood-sucking
- Weakens adult bees
- Damages growing larval bees resulting in deformities
Control
- Acaricidal strips hung between combs
- Destoy colonies in apiary (if isolated outbreak)
- Monitor mite numbers and treat if widespread