Tuberculosis - Cattle
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
- Caused by Mycobacterium bovis and M. tuberculosis
- Reside primarily within macrophages where they multiply and result in characteristic granulomatous inflammation (macrophages and giant cells, epithelioid cells)
- Cattle can be infected by inhalation of the organism or through milk
- The primary complex
- Describes the initial focus of infection at the portal of entry (lungs) plus involvement of regional lymph nodes
- 90% of cases exhibit the pulmonary form
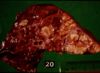
- Grossly:
- Small tubercles in dorsocaudal subpleural areas which progress to larger confluent areas of caseous necrosis
- Usually start at bronchio-alveolar junction an progress to the alveoli
- Caseous lesions, may calcify or be encapsulated
- Multiple foci may coalesce
- Ulcers in trachea and bronchi due to coughed up bacteria
- Spreads into pleura
- Microscopically:
- Typical granulomatous inflammation
- Epitheliod and giant cells at centre of tubercles
- Macrophages with ingested bacteria, forming epithelioid cells - large vesicular nuclei, abundant pale cytoplasm
- Giant cells, formed by fusion of macrophages, with multiple nuclei
- Narrow layer of lymphocytes, mononuclear cells and plasma cells at the periphery of the tubercle
- With time, peripheral fibroplasia and central necrosis develop
- If the infection is not contained in the primary complex described above, the mycobacteria can disseminate via lymphatics to other organs and lymph nodes
- This can allow the development of miliary tuberculosis, i.e. numerous small foci of infection in many organs/ tissues