Avian Medicine Q&A 11
Revision as of 12:33, 29 June 2011 by Lwyasm1 (talk | contribs) (Created page with "<br style="clear:both;" /> {| align="left" width="100%" style="background-color:#04B4AE" |- | align="center" | 90px|Mansonlogo | align="left" | This ques...")
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more |
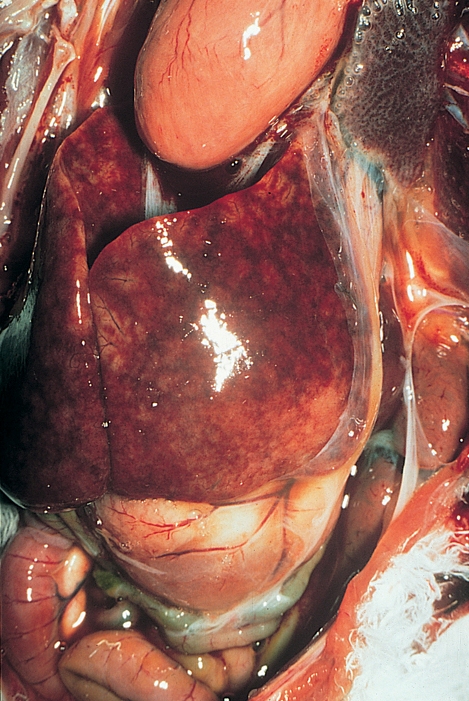
An African grey parrot died following a subacute illness characterized by respiratory signs and elevated SGOT and
creatinine phosphokinase (CPK). At necropsy, the lungs were wet, the spleen was enlarged and the liver was enlarged and mottled.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What infectious agents should be considered in the differential diagnosis? | Severe hepatitis should lead to a consideration of viral infections, such as Pacheco’s disease, bacterial infections, chlamydiosis and systemic protozoal infections.
|
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| What histological features can be used for a definitive diagnosis of each of the above, and what organs should be submitted? | In the liver, the pattern of inflammation/necrosis, occurrence of micro-organisms and inclusion body formation can be used for diagnosis. The spleen and lungs should also be examined as each of the potential causes leads to differential changes in these organs
|
[[|Link to Article]] | |