Crustacea
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
Introduction
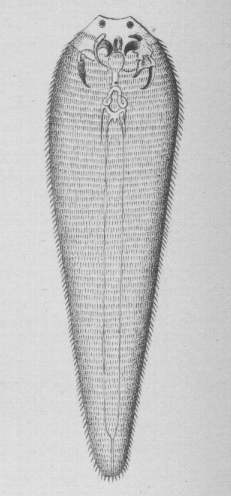
Linguatula serrata
- Also known as the 'tongue worm'
Recognition
- Tongue-like appearance
- Expanded anteriorly
- Adults are over 10cm in length
- Females measure betwen 30-130mm in length
- Males measure up to 20mm in length
- Transversely striated
Life Cycle
- 6 month life cycle
- Adults inhabit the nasal passages of dogs and sometimes cats
- Eggs are expelled by coughing and sneezing or are passed out with the faeces
- Herbivorous intermediate hosts ingest the eggs
- Eggs hatch in the herbivore intestine
- Larvae migrate to the mesenteric lymph nodes and encyst to become infective nymphs
- Cysts measure 1mm in diameter
- When a dog eats infeced uncooked viscera the life cycle is completed
- Infective nymphs migrate from the viscera during chewing and crawl up into the nasal cavity via the soft palate
- Infective nymphs mature to adults in the nasal cavities and can survive for a year in the final host
Pathogenesis
- Causes rhinitis
- Heavy infection leads to coughing, sneezing and nasal discharge