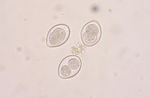
Coccidia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
Eimeria spp.
Isospora spp.
Coccidia of Poultry
Other Avian Coccidia
Coccidia of Sheep
- Different species of Eimeria occurs in sheep and goats
Coccidia of Goats
- Many Eimeria species
- 2 Eimeria are pathogenic
- Cause diarrhoea and a decreased growth rate
- Different species of Eimeria occurs in sheep and goats
Coccidia of Horses
- Only one atypical Eiemria
- Forms large subepithelial gametocytes in villi
- Large, dark coloured oocysts
- Approximately 12μm
- Occasionally causes diarrhoea
Coccidia of Pigs
Coccidia of Dogs
Coccidia of Cats
Coccidia of Rabbits
- Besnoitia bennetti in larynx of horses
- Hepatozoon americanum and subclinical H. canis in periosteal bone formation
- Both are Tick borne diseases
- H. canis – Rhipicephalus sanguineus
- Ticks become infected by ingesting a blood meal containing macrophages and neutrophils infected with the parasite gamonts -> sexual replication in the gut of the tick -> oocysts containing infective sporozoites -> dogs ingest the tick schizogony occurs in numerous tissues.
- Both are Tick borne diseases