Principles of Fluid Therapy
| This article is still under construction. |
What is Fluid Therapy?
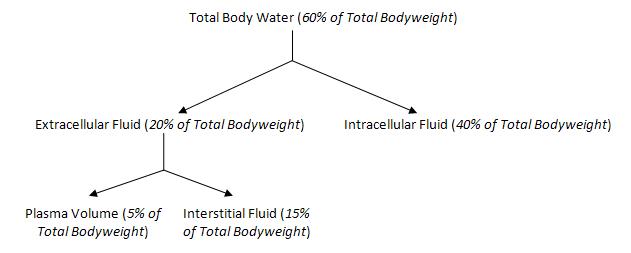
Fluid Therapy is the administration of fluids to a patient as a treatment or preventative measure. It can be administered via an intravenous, intraperitoneal and subcutaneous routes. 60% of total bodyweight is accounted for by the total body water. This can further be divided into intracellular or extracellular as shown below.
Fluid therapy is indicated when there is a loss of fluid to any part of these compartments. The severity of the fluid loss, and the compartment which is has been lost from with influence the choice of fluid.
Indications
- Hypotension
- Hypovolemia
- Electrolyte, metabolic and acid base disorders
- Decreased oxygen delivery
- Geriatric patients at risk of organ failure
Definitions
- Osmosis is the net movement of water across a semi permeable membrane. The movement is caused by a concentration gradient due to different solute concentrations.
- Osmotic Pressure is the pressure caused by the solutes within the solution. The solute concentration prevents water movement across the membrane.
- Tonicity is the term used to compare the osmotic pressure of different solutions
- A hypotonic solution is one that has an osmotic pressure lower than plasma.
- A isotonic solution is one that has an osmotic pressure the same than plasma.
- A hypertonic solution is one that has an osmotic pressure higher than plasma.
Types of Fluids
- Crystalloids
- Colloids
- Blood Products
Fluid Rate Calculations
When calculating the fluid requirements of a patient, there are 3 elements to consider -
- Replacement
- Maintainance
- Ongoing Losses
Replacements are calculated based on the level of dehydration. Dehydration is based upon clinical assessment of each individual patient. Most commonly, skin tent is used for assessment. To calculate the amount required for replacement within a 24 hour period, the percentage dehydration is used in the following calculation.
| Replacement = % Dehydration x Bodyweight (kg) x 10 |
|---|
Maintainance is the basic rate which a patient requires during a 24 hour period. It is commonly calculated as 50ml/kg/24hr, or 2ml/kg/hr.
Ongoing losses are calculated based on a predicted fluid amount lost by a patient within a 24 hour period. Common losses include vomitting and diarrhoea. It is often helpful here if the owners are able to give a detailed history as this makes it easier to predict the pattern of losses. To calculate the fluid requirement, the following calculation is used.
| Ongoing losses = Amount per loss (ml/kg) x Bodyweight (kg) x No. of losses |
|---|