| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Introduction
Myiasis is the parasitism of living animals by dipteran larvae. Myiasis can be obligatory or facultative (optional) and is described as cutaneous, nasal or somatic.
Screw Worm Myiasis
- C. bezziana cause myiasis in both animals and humans
- Located mainly in tropical regions
- Larvae are obligate parasites
Recognition
- Similar to Calliphora spp.
- Iridescent
- Clear wings
- Blue abdomen
- Longitudinal stripes on thorax
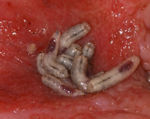
- Larvae have bands of spines
- Look like screws
Life cycle
- Eggs laid in wounds or body cavities
- Larvae feed as colonies
- Larvae drop to the ground to pupate
Pathogenesis
- Spiracles are exposed as larvae feed which expands the wound
- Creates a foul smelling lesion
- Cause irritation and pyrexia
Control
- In the USA
- Mass eradication through the release of sterile males
- Currently only persists where flies have migrated across the Mexican border
- In Africa
- Introduced into Libya through the importation of infested livestock
- Sterile males released
- Eradication occurred in 1991
Maggot Debridement Therapy
- Human medicine
- Sterile Lucilia sericata maggots used to treat infected and necrotic wounds
- Larvae secrete proteolytic enzymes and antimicrobial agents into the wound
- Larvae do not burrow under the skin or attack healthy tissue
- Veterinary medicine
- Published reports rare
- Recently used successfully to treat a suppurative wound in a donkey that did not respond to conventional medical methods and surgery
Wohlfahrtia spp.
- Obligatory parasite
- Occurs in North America
- Parasite of mink and sometimes humans
Recognition
- Large 8-14mm long
- Pale grey
- Black stripes on thorax
- Black spots on abdomen
Life cycle
- Larvae deposited directly onto host
- No egg stage
- Larvae moult twice on host then fall to ground to pupate
Pathogenesis
- Larvae penetrate intact skin
- Cause boil like swellings