| This article is still under construction. |
Overview
Helicobacter spp. are related to Campylobacter species and Arcobacter species and are pathogens affecting the stomach.Unlike many bacterial pathogens Helicobacter spp. are able to survive in the extremely low pH environment that exists within the stomach. The genus was first discovered in the stomach of humans in 1987. There are several species identified in humans and many veterinary species where the incidence of some species of Helicobacter is high. Species such as H. felis, H. bizzozeronii, H. salomonis and H. bilis have been identified in the gastric mucosa and intestines of dogs and cats. The genus is however considered of low pathogenic significance in veterinary species but there is possibility of zoonosis of the H. pylori species that is the causitve agent of gastric disease in humans. However H.pylori has not been identified in cats and is rarely seen in cats. The major veterinary concern posed by Helicobacter spp. is the H. mustelae that has been associated with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers in ferrets.
- Discovered in the stomach of humans in 1987
Characteristics
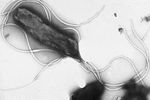
Helicobacter are gram negative rod bacteria, they can appear helical, S-shaped or curved.
- Helical, S-shaped or curved Gram negative rods
- Require enriched media; some grow on Skirrow agar
- Microaerophilic, non-saccharolytic
- Oxidase positive and catalase positive except for H. canis
- Helicobacters which colonise gastric mucosa are urease positive
Clinical infections
The significance of Helicobacter spp. in gastointestinal disease of domestic carnivores is unknown. Up to 80% of clinically healthy dogs have Helicobacter spp. present, several species have been identified in the dog such as;H. felis, H. bizzozeronii, H. salomonis and H. bilis. Experimental infection of dogs has failed to show a consistent relationship between infection with Helicobacter and the development of pathology. The only species known to be of veterinary importance is H. mustelae which has been associated with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers in ferrets. Helicobacter pylori infects humans causing gastritis as well as gastric and duodenal ulcers. It has also been associated with gastric adenocarcinoma in humans however There is no evidence for this in animals.