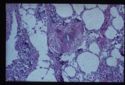
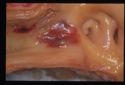
Presence of inflammatory cells within and around the vessel wall. Vasculitis often increases vessel permeability, presenting as oedema and haemorrhage. Petichial and ecchymotic haemorrhages within mucosae are characteristic.
Multiple aetiologies:
Infective
- Bacterial: Often toxin damage E.g. Salmonellosis, Erysipelas.
- Viral: Epitheliotropic viruses E.g. Equine arteritis, Canine distemper.
- Mycotic: Mucormycosis.
Parasitic
The main parasitic lesion of the arteries in th UK is Strongylus vulgaris of horses. Larvae and mmatures migrate along arterial walls, particularly cranial mesenteric and ilio-caecal arteries with occasional aberrent migration to the ascending aorta.