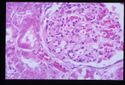
Polyarteritis nodosa
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fibrinoid necrosis of the media of arteries and arterioles. An intense neutrophil infiltration may be identified which, when the lesions become chronic, is accompanied by cells such as eosinophils, plasma cells and lymphocytes.
Aetiology unknown but thought to be an antibody-antigen reaction.
Fibrinoid necrosis is also a feature of vessel damage. Seen with uraemia in dogs where the ammonia within the bloodstream irritates the endothelial layer. The affected arteries include the gastric arteries which, when damaged, result in ischaemia and gastric ulceration.