Male Reproductive Anatomy - Donkey
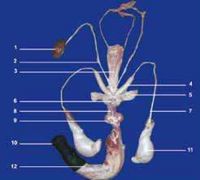
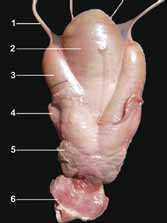
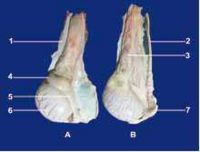
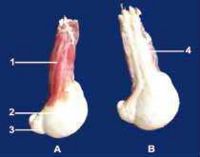
The reproductive organs of the jack are larger than a stallion’s. In the adult North African donkey, the bulbo-urethral gland’s length and width range from 2.8 to 3.5 and 3.5 to 5 cm respectively. The prostate measures 3.8 to 6 cm in length, 2.6 to 3.5cm in width and 1.6 to 2.5 cm in thickness. The vesicular glands (seminal vesicles) measure 5 to 13 cm in length and 2.5 to 4 cm in diameter. The ampullae of the vas deferens are 10 to 13.5 cm in length and 1.6 to 2.5 cm in diameter. During erection and ejaculation, the glans penis presents a more pronounced dilation. Video-endoscopic examination shows a more prominent colliculus seminalis.
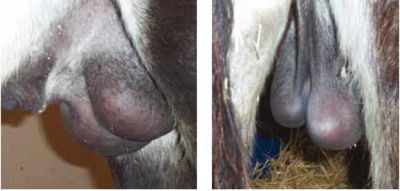
The scrotum is more pendulant and the testicles and epididymis are larger than in horses, but present similar ultrasonographic features. Testicular measurements for the most common breeds range from 6 to 7.5 cm for the height, 9 to 10.5 cm for the length and 4.8 to 6 cm for the width (Carluccio et al, 2004; Tibary et al, 2005). The epididymal tail is more prominent than that of the stallion.
Click here to view ultrasound images of male urogenital organs.
References
- Tibary, A., Sghiri, A. & Bakkoury, M. (2008) Reproduction In Svendsen, E.D., Duncan, J. and Hadrill, D. (2008) The Professional Handbook of the Donkey, 4th edition, Whittet Books, Chapter 17
- Carluccio, A., Villani, M., Contri, A., Tosi, U., and Battocchio, M. (2004). ‘Preliminary study on some seminal and testicular morphometric characteristics in Martina Franca jackass’. Ippologia 15. pp 23-26.
- Tibary, A., Bakkoury, M., Anouassi, A., and Sghiri, A. (2005). ‘Examen et évaluation de l’aptitude à la reproduction’. Reproduction Equine Tome II: L’ Etalon. A. Tibary, M. Bakkoury (eds). Actes Editions, IAV Hassan II, Maroc, 2005. pp 167-174.
|
|
This page was sponsored and content provided by THE DONKEY SANCTUARY |
|---|