Primary
- Primary hyperparathyroidism is caused by glandular hyperplasia or neoplasia.
- Rare.
Secondary
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism causes fibrous osteodystrophy or "rubber jaw".
- In secondary hyperparathyroidism, the gland is overactive due to another condition coexisting in the body, rather than a primary parathyroid gland defect.
- There are two common forms of secondary hyperparathyroisism:
- Both forms result in increased osteoclastic resorption of bone and deposition of fibro-osteoid matrix that fails to mineralise.
- Flat bones of the skull swell.
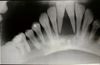
- Fibrous tissue is seen around the tooth roots.
- Bone softens in adult animals.
- This is what gives rise to the term "rubber jaw".
- Long bones become soft with thin cortices.
- These fracture easily.
Nutritional Hyperparathyroidism
- Nutritional hyperparathyroidism is also known as nutritional osteodystrophy.
- This occurs most commonly in:
- Young, fast-growing animals
- Animals with a poor diet, for example:
- Swine fed unsupplemented cereal grain
- Dogs and cats fed all-meat diets
- Horses fed bran
- In this case, nutritional hyperparathyroidism is known as "bran disease".
Pathogenesis
- Pathogenesis follows low calcium/high phosphate diets.
- These lead to decreased serum calcium levels, stimulating PTH release.
- The increase in PTH gives an increase in bone resorption, causing pathology.
Pathology
- Gross
- Severe cases may show:
- Maxillary and mandibular swelling
- Teeth lost or buried in soft tissue
- Nasal and frontal bone enlargement, leading to dyspnoea
- Long bone fracture
- Detatchment tendons and ligaments
- Early or less severe cases are characterised by shifting lameness and ill thrift.
- Severe cases may show:
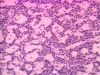
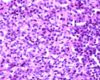
- Histological
- Osteoclastic resorption
- Fibrous replacement
Metabolic Bone Disease
Renal Hyperparathyroidism
- Renal Hyerparathyroidism is mostly seen in the dog as an expression of chronic renal disease.
Pathogenesis
- Chronic renal disease results in reduced glomerular filtration.
- As glomerular filtration is reduced, phosphate is retained. Chronic renal failure also causes inadequate vitamin D production in the kidneys.
- Hyperphosphataemia develops due to phosphate retention.
- Hypocalcaemia also occurs, as high levels of phosphate depress calcium levels.
- PTH is released in an attempt to maintain the correct blood calcium:phosphorous ratio. This can have several effects:
- Parathyroid hyperplasia
- I.e. renal secondary hyperparathyroidism.
- Soft tissue mineralisation
- Particularly seen in dogs
- Calcium is commonly deposited in the subpleural connective tissue of the intercostal spaces.
- Calcification also occurs in other sites, e.g. stomach wall, lungs, kidneys.
- Increased bone resorption
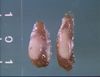
- This causes fibrous osteodystrophy, or "rubber jaw".
- Parathyroid hyperplasia
Pathology
- Pathology seen in renal hyperparathyroidism is very similar to that seen in nutritional hyperparathyroidism.
- Gross
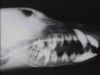
- The major gross presentation is a fibrous osetodystrophy, or rubber jaw.
- The maxillae and mandible appear swollen.
- Radiographically, bone shows reduced density, and teeth hence appear embedded in soft tissue.
- However, only a few cases of chronic renal disease show such severe bone lesions.
- Other lesions may also be seen.
- Intercostal muscles may be calcified.
- Bone marrow lesions may cause anaemia.
- The lung may show oedema, and have calcified alveolar walls.
- The major gross presentation is a fibrous osetodystrophy, or rubber jaw.
- Histological
- Osteoclastic resorption
- Fibrous replacement