|
|
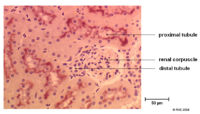
Glomerulus
- Made up of many parallel capillaries
- These capillaries do not connect to venules as with other capillaries
- Blood flows into these capillaries through a wide afferent arteriole and leaves through a narrower efferent arteriole
- The flow from the efferant arteriole enters the peritubular capillaries surrounding the Proximal Tubule
- This change in diameter maintains a high filtration pressure which is essential for filtration
- Also the blood entering the afferent arteriole is at very high pressure already as it from the renal artery
- The pressure actually forces molecules through the glomerular filtration barrier which is responsible for selectively filtering the blood forming the glomerular filtrate.
- As well as the the cells in the blood vessels the other component of the glomerulus are the mesangial cells:
- These give support to the glomerulus
- Maintain glomerular basal lamina
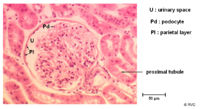
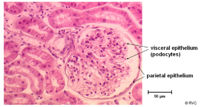
Bowmans Capsule
- Surrounds the capillaries of the glomerulus
- Has two layers
- Inner visceral layer - Podocytes
- Outer parietal layer
- It is here where the filtrate is collected before entering the proximal tubule