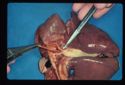
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
|
|
- Occurs in all animals
- Young animals have a greater risk
- Very common in dogs
- Not very common in cats
Signalment
Genetics & Predisposed Breeds: Toy Breeds (Yorkshire Terrier, Pomeranian, Maltese, Toy Poodles); Miniature Poodles, Shetland Sheepdogs, German Shepherds, Collies
- Greater occurrence in females
Description
- Persistence of the ductus arteriosus after birth
- During fetal life, the ductus arteriosus connects the pulmonary artery to the descending aorta. This fetal vessel allows most of the blood to bypass the developing lungs and go directly to the aorta and systemic circulation. In fetal life oxygen is provided by the placenta while the lungs are developing.
- At birth, the animal takes a breath of air and uses its lungs for the first time. High levels of oxygen from the pulmonary vasculature enter the circulation and the ductus arteriosus responds by contracting the smooth muscles lining its vessel wall. The functional closure of the ductus arteriosus occurs within 2-3 days after birth and with time it will become an anatomical closure. However, some animals have a ductus arteriosus that doesn't respond to the increased oxygen at birth and remains open (patent).
- After birth PDA causes a reversal of blood flow from the higher pressure of the descending aorta through the ductus arteriosus to the pulmonary artery and into the lungs. This is known as left-to-right shunting. The shunting of blood in this manner overwhelms the pulmonary vasculature and the left side of the heart. The increased volume of blood from the lungs travels to the left atrium and left ventricle which respond to the added pressure by dilation and hypertrophy. As a result, PDA can eventually lead to pulmonary edema and left-sided congestive heart failure.
- Normally the pulmonary circulation is equipped to handle increased volumes of blood without pulmonary arterial pressure changes. However, sometimes the increased blood volume in the lungs causes gross changes to the pulmonary arterioles causing pulmonary hypertension and raised pulmonary arterial pressures. If the pressure is high enough, it can cause a reverse PDA (right-to-left shunt) and unoxygenated blood will bypass the lungs heading straight for the descending aorta and the systemic circulation.
Diagnosis
History & Clinical Signs
-Signs of left sided congestive heart failure
-Exercise intolerance
-Differential cyanosis (Reverse PDA)
-Hindlimb weakness (Reverse PDA)
-Asymptomatic
Physical Exam
PDA
-Systolic & diastolic continuous machinery murmur (Left side of the heart is the loudest)
-Precordial thrill (Palpable after a murmur)
-Waterhammer pulses (A forceful pulse that immediately collapses)
Reverse PDA
-Differential cyanosis (Normal oral mucus membranes, cyanotic membranes everywhere else)
-Hyperviscosity (Increased PCV from hypoxia-mediated polycythemia)
Radiographic Findings
PDA
-Left atrial & ventricular enlargement
-Pulmonary overcirculation
-Dorsoventral view shows three bulges: aorta (1 o’clock), pulmonary artery (2 o’clock), left auricle (3 o’clock) positions
-Signs of left-sided congestive heart failure (pulmonary congestion, edema)
Reverse PDA
-Right ventricular enlargement
-Dilation of the pulmonary trunk and arteries
-Left ventricular enlargement
Echocardiographic Findings
PDA
-Left atrial & ventricular enlargement
-Dilation of pulmonary artery
-PDA might be visualized
Doppler can show abnormal flow
Reverse PDA
-Right ventricular enlargement
-Left ventricular enlargement
Doppler can show abnormal flow
Electrocardiographic (ECG)
PDA
-Classic signs for left atrial enlargement (wide P wave)
- Classic signs for left ventricular enlargement (tall R wave, wide QRS)
-Atrial & ventricular arrhythmias may be present
Reverse PDA
-Classic signs of right sided heart enlargement
Treatment
PDA
-Surgical ligation of the ductus arteriosus (2-4 months of age)
-Animals with congestive heart failure need stabilization of heart failure before surgery
Reverse PDA
-Surgery is contraindicated
-Exercise Restriction
-Phlebotomy (Bleeding to keep PCV at normal levels)
Prognosis
PDA
-Very good prognosis with surgical treatment
-Poor prognosis if large PDAs are left untreated
Reverse PDA
-Poor prognosis