Ribs and Sternum - Anatomy & Physiology
|
|
Costae
- Arranged in pairs and articulate with two successive vertebrae
- Bony dorsal part, body of rib, and ventral costal cartilage
- Increase in length, curvature and amount of cartilage craniocaudally
- Cartilage of last rib may fail to join that of its neighbor: said to be floating
- Join ventrally on the midline at the Sternum, which is comprised of three parts
- Manubrium: most cranial, projects beyond the first set of ribs and can be palpated
- Body: segmented sternebrae joined by cartilage in young animals that is later replaced by bone
- Xiphoid Cartilage: caudal end that projects between lower ends of costal arches, providing attachment for the linea alba
- Costal Joints:
- Costovertebral joint: head of rib articulates with vertebral column, ball and socket with very restricted mobility
- Costotransverse joint: tubercle articulates with vertebra, sliding joint
- Costosternal joints:
- Interchondral joints: asternal ribs, elastic syndesmoses
- Intersternal joints: impermanent synchondroses
Thoracic Musculature
- Primarily concerned with respiration
- Inspiratory muscles enlarge the thoracic cavity
- Expiratory muscles diminish the cavity and force air out
- The most important thoracic muscle is the Diaphragm, which separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities
- Intercostal muscles
- Dome-shaped, convex on its cranial surface
- Central tendon forms the vertex
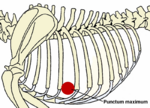
- Neutral position (between full inspiration and full expiration): 6th rib behind the olecranon
- Attaches via muscular periphery to the costal arch
- Three openings:
- Aortic hilus conveying the aorta, azygous vien, and thoracic duct
- Oesophageal hiatus conveying the oesophagus, vagal trunks and supplying vessels
- Caval foramen within central tendon conveying caudal vena cava
- Innervated by the phrenic nerve, which arises from the caudal cervical nerves (C5-C7)
- Three openings:
- External fibers run caudoventrally and internal fibers run cranioventrally
- Each is confined to a single intercostal space
- Transversus thoracis arises from and covers the dorsal sternum and inserts on sternal ribs close to the costochondral junctions
- Rectus thoracis covers the ends of the first four ribs in continuation of the rectus abdominus
- Serratus dorsalis overlies the dorsal aspect of the ribs
- Innervation of these muscles is supplied by the Intercostal nerves, which are ventral branches of the thoracic spinal nerves
Abdominal Musculature
- Ventrolateral Muscles: flanks and abdominal floor
- All muscles join via aponeuroses in the linea alba at midline, which runs from the xiphoid process to the pelvic symphysis via the prepubic tendon, ensheathing the rectus abdominus
- The External abdominal oblique runs caudoventrally from the lateral surface of the ribs and the lumbar fascia to the linea alba. Its caudal border is thickened to form the inguinal ligament and a slit in its aponeurosis forms the superficial inguinal ring.
- The Internal abdominal oblique runs cranioventrally from the tuber coxae and the thoracolumbar fascia to the linea alba. It forms the cranial border of the inguinal canal.
- The Transversus abdominus is the deepest muscle of the flank, running dorsoventrally from the inner surface of the last ribs and the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae.
- The Rectus abdominus forms a broad band parallel to the linea alba, arising from the ventral costal cartilages and inserting on the prepubic tendon. It also forms the medial border of the inguinal canal.
- Sublumbar Muscles:
- Psoas minor: stabilizer of the vertebral column, may also rotate the pelvis at the sacroiliac joint
- Psoas major and Iliacus: