Sporotrichosis
Revision as of 13:37, 29 April 2010 by Bara (talk | contribs) (Created page with 'thumb|right|150px|Sporotrichosis in a horse -Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath [[Image:Sporotrichosis…')
- Sporothrix schenckii
- Occurs in soil, wood and vegetation
- Saprophyte of both decaying and healthy vegetation
- Worldwide
- Exogenous infections through wounds
- Sporadic infections
- Non-contageous
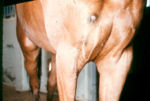
- Causes subcutaneous nodules or granulomas
- Nodules ulcerate discharging pus
- Spread via the lymphatics
- The bones and viscera can be involved which terminates in mortality
- This is rare
- Reported in dogs and horses
- Affects dogs, horses, cats, monkeys, mules, camels, donkeys, cattle, fowl and rodents
- Most commonly seen in horses as an ascending lymphocutaneous infection of the legs
- Can be confused with epizootic lymphangitis in horses
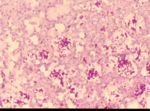
- Single cell, cigar shaped
- Usually found within neutrophils
- Yeast cell clusters with peripheral eosinophilic rays can be seen in tissue sections
- Stained using PAS, Gram stain (positive), fluorescent antibody and Calcofluor White
- Latex agglutination and immunodiffusion serology can be performed
- Grows on Blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar in one to three weeks
- At 37°C:
- Colonies are smooth, cream to tan coloured and soft
- No mycelium can be seen
- At 25°C to 27°C:
- Colonies turn from white and soft to tan to brown to black
- Leathery, wrinkled and coarse
- Mycelium can be seen as branching septate hyphae
- Conidiospores can also be seen
- At 37°C:
- Potassium iodide treatment orally
- 5-fluorocytosine and amphotericin B can also be used