Difference between revisions of "Feline Medicine Q&A 07"
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:Manson Sparkes}} | {{Template:Manson Sparkes}} | ||
| − | [[Image:|centre|500px]] | + | [[Image:Feline Medicine 07.jpg|centre|500px]] |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*Oesophagitis can occur secondary to persistent vomiting, secondary to reflux of gastric juice, secondary to hiatal hernia, and following ingestion of caustic substances. | *Oesophagitis can occur secondary to persistent vomiting, secondary to reflux of gastric juice, secondary to hiatal hernia, and following ingestion of caustic substances. | ||
*Oesophageal motility disorders include primary megaoesophagus, myasthenia gravis, dysautonomia, and polymyopathy. Of these potential causes, acute onset regurgitation in a young cat would be most commonly due to oesophagitis, oesophageal stricture, foreign body, anterior mediastinal lymphoma, primary megaoesophagus, and persistent right aortic arch. The recent onset of signs would suggest the latter two are less likely. | *Oesophageal motility disorders include primary megaoesophagus, myasthenia gravis, dysautonomia, and polymyopathy. Of these potential causes, acute onset regurgitation in a young cat would be most commonly due to oesophagitis, oesophageal stricture, foreign body, anterior mediastinal lymphoma, primary megaoesophagus, and persistent right aortic arch. The recent onset of signs would suggest the latter two are less likely. | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1=Regurgitation |
|q2=What can be seen on the contrast oesophagram taken after the cat was offered food mixed with barium? Suggest a likely diagnosis. | |q2=What can be seen on the contrast oesophagram taken after the cat was offered food mixed with barium? Suggest a likely diagnosis. | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
Latest revision as of 16:54, 9 September 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Feline Medicine questions |
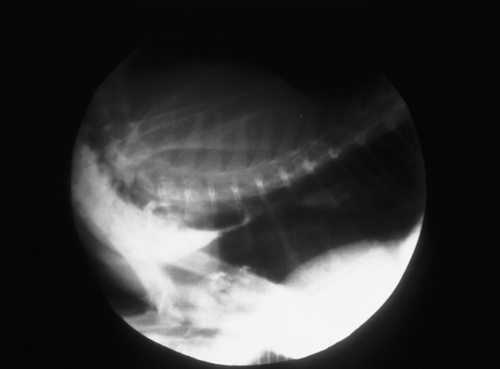
A 6-month-old neutered male Balinese cat presents with recent onset persistent regurgitation after feeding.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What are the differential diagnoses? | There are many differential diagnoses for regurgitation, but they can broadly be divided into obstructive disorders (luminal, mural, and extramural), inflammatory disease, and motility disorders.
|
Link to Article | |
| What can be seen on the contrast oesophagram taken after the cat was offered food mixed with barium? Suggest a likely diagnosis. | The spot fluoroscopy film demonstrates accumulation of a barium bolus in the cervical and proximal thoracic oesophagus, cranial to a tapered area of barium typical of a stricture. The narrowed area is too far cranial to be due to a persistent right aortic arch. This cat had been anaesthetized for castration 2 weeks previously, and this was a post-anaesthetic (reflux) stricture. |
Link to Article | |
| What would be a suitable treatment regimen? | Optimal treatment for this case would be repeat balloon dilation of the stricture (several dilations may be required initially at 2–3 day intervals but less frequently as the condition improves), combined with medical therapy. This comprises a mucosal protectant (e.g. sucralfate), an H2-blocker (e.g. famotidine), anti-inflammatory doses of prednisolone, possibly colchicine (to inhibit fibrosis and stricture reformation), and a low-fat diet to encourage gastric emptying. |
Link to Article | |