Difference between revisions of "Fluoroquinolones"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
}} | }} | ||
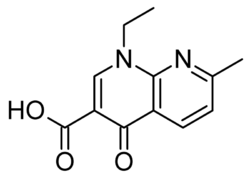
| + | [[Image: Nalidixic Acid.png|thumb|right|250px|Nalidixic Acid - The Parent Drug of the Fluoroquinolones]] | ||
The parent drug of the quinolone family was '''Nalidixic acid''', this was found to be very narrow spectrum. It worked well only against gram negative enterobacteriaceae and resistance quickly developed. This limited it's use now for just urinary tract infections and for treatment of ''Aeromonas salmonicida'' in fish. Due to the restricted spectrum of the quinolones fluoroquinolones were developed to increase the range. The most commonly used in practice are '''Enrofloxacin, Marbofloxacin, Danofloxacin, Difloxacin, Ibafloxacin and Orbifloxacin.''' | The parent drug of the quinolone family was '''Nalidixic acid''', this was found to be very narrow spectrum. It worked well only against gram negative enterobacteriaceae and resistance quickly developed. This limited it's use now for just urinary tract infections and for treatment of ''Aeromonas salmonicida'' in fish. Due to the restricted spectrum of the quinolones fluoroquinolones were developed to increase the range. The most commonly used in practice are '''Enrofloxacin, Marbofloxacin, Danofloxacin, Difloxacin, Ibafloxacin and Orbifloxacin.''' | ||
Revision as of 09:06, 24 October 2008
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
The parent drug of the quinolone family was Nalidixic acid, this was found to be very narrow spectrum. It worked well only against gram negative enterobacteriaceae and resistance quickly developed. This limited it's use now for just urinary tract infections and for treatment of Aeromonas salmonicida in fish. Due to the restricted spectrum of the quinolones fluoroquinolones were developed to increase the range. The most commonly used in practice are Enrofloxacin, Marbofloxacin, Danofloxacin, Difloxacin, Ibafloxacin and Orbifloxacin.