Impaction of the Oesophagus
| Also known as: | Choke |
Description
Impaction/obstruction of the oesophagus or 'choke' is the most common oesophageal disease of cattle and horses. The most common sites of obstruction are the thoracic inlet, the base of the heart, and the hiatus oesophagus of the diaphragm. In horses, causes of choke include consumption of unsoaked sugarbeet, rapid ingestion of roughage (hay), indadequate mastication of food, or rarely the ingestion of a foreign body (e.g. corn cob). Horses that are poorly fed or have poor dentition are more prone to the condition.
Clinical Signs
Horse
Although the presentation of a horse with choke may be dramatic, it does not constitute an emergency. The typical sign of choke is dysphagia with regurgitation of food and saliva through the nostrils. Acute onset pain may manifest through alterations in posture such as an arched neck or abducted elbows. The horse may appear anxious, grunt frequently and make repeated attempts to swallow. If the condition has become long-standing, foetid breath may be apparent. If accompanied by pyrexia, this may indicate the development of aspiration pneumonia.
Cattle
Oesophageal obstruction in cattle is a more serious condition than in the horse. Obstruction leads to failure to eructatate which may lead to bloat.
Dog
- Usually with small bones
- Animals that feel protective of feed may gulp food down quickly, particularly if given small chops / knuckle bones.
- Knobbly shape may make bone lodge in oesophagus, particularly just anterior to heart.
- Very difficult to dislodge (because of shape).
- Pressure necrosis occurs very quickly around it and can erode through oesophagus within about 24 hours.
- Small bone may also lodge in duodenum if they pass through the stomach.
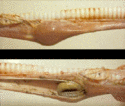
Diagnosis
An initial diagnosis of choke in any animal may be suspected if the above clinical signs are present with a history of acute onset pain and access to unsuitable food. If the obstruction has led to the accumulation of food material in the oesophagus, a mass may be palpable on the left ventrolateral aspect of the neck. Confirmation of the diagnosis may be achieved by the inability to pass a nasogastric tube or direct visualisation of the obstruction using endoscopy.