Difference between revisions of "Lizard Cystic Calculi"
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
'''Examination''' | '''Examination''' | ||
| − | + | Symptoms of cystic calculi may be similar to those of kidney disease. Cystic calculi may be palpated on physical examination. | |
Revision as of 00:37, 27 February 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
Introduction
Cystic calculi are commonly seen in lizards fed unbalanced diets but dehydration and cystitis may be involved. A commonly associated disease is renal failure.
This disease may have a multifactorial aetiology. The stones are usually urates since lizards, like most reptiles, are uricotelic.
Dealing with cystic calculi
Examination
Symptoms of cystic calculi may be similar to those of kidney disease. Cystic calculi may be palpated on physical examination.
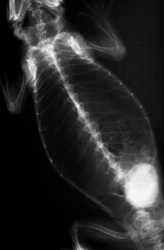
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on palpation of a mass in the coelomic cavity and radiography showing a radiopaque mass that has concentric layers.
Therapy
Coeliotomy and cystotomy.
The length of the skin incision should be 1.5 times the diameter of the largest stone. The bladder is thin-walled and stay sutures facilitate handling of the bladder and closing the incision. The bladder wall is closed with a two layer pattern.
Bacterial culture and stone analysis are recommended. Carry out supportive care.
Prevention
As well as species-specific diet and husbandry, it is recommended to limit uric acid precursors. As uric acid is produced from all proteins (and not just the nuclear proteins as in mammals) it has been advised not to feed diets that are high in protein. It has also been advised to especially limit foods that are high in purines such as asparagus, mushrooms, offal, anchovies and sardines.