Difference between revisions of "Maltese terrier cross with enlarged abdomen"
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
:abdominal enlargement, lethargy, inappetance for 3 months. Your physical exam shows an obviously distended abdomen with a very large (>10 cm diameter) firm palpable abdominal mass, mucous membranes pink but paler than normal, periodontal disease. Otherwise clinical exam within normal limits, and she seems surprisingly alert and responsive. The clients say the abdominal enlargement has only happened in the past month. | :abdominal enlargement, lethargy, inappetance for 3 months. Your physical exam shows an obviously distended abdomen with a very large (>10 cm diameter) firm palpable abdominal mass, mucous membranes pink but paler than normal, periodontal disease. Otherwise clinical exam within normal limits, and she seems surprisingly alert and responsive. The clients say the abdominal enlargement has only happened in the past month. | ||
</big></b> | </big></b> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<center><WikiQuiz | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| Line 80: | Line 60: | ||
! Haematology report | ! Haematology report | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[File:Case 22 haematology.jpg| | + | | [[File:Case 22 haematology.jpg|800px]] |
|} | |} | ||
{| class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed wikitable" | {| class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed wikitable" | ||
! Serum biochemistry report | ! Serum biochemistry report | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[Case 22 biochemistry.jpg| | + | | [[File:Case 22 biochemistry.jpg|800px]] |
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | ! ||Blood donor qualities | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | a) ||healthy, receives yearly physical exam, CBC, UA, biochemistry | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | b) ||not been the recipient of a transfusion | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | c) ||over 25kg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | d) ||negative for DEA1.1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | e) ||fully vaccinated, heartworm negative, dogs receiving heartworm prophylaxis | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | f) ||screened for Ehrlichia and Babesia (in areas where these occur | ||
|} | |} | ||
<center><WikiQuiz | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
questionnumber="3" | questionnumber="3" | ||
| − | question="" | + | question="Your next tests are haematology and serum biochemistry. You give the option of referral for surgery but the clients decline. You are not sure what to expect at surgery so you hire a suction unit and electrocautery unit from a drug company. You ask the clients to bring in their friend's dog so you have a whole blood transfusion on hand if needed. What qualities should you look for in choosing a blood donor for your surgical patient? (Select from the table above.)" |
| − | choice1="" | + | choice1="a, c, d" |
| − | choice2="" | + | choice2="a, b, c" |
| − | choice3="" | + | choice3="a, c, d, e" |
| + | choice4="a, e, f" | ||
| + | choice5="a, b, c, d, e, f" | ||
| + | correctchoice="5" | ||
| + | feedback1="Correct, but there are other qualities you should look for. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback2="Correct, but there are other qualities you should look for. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="Correct, but there are other qualities you should look for. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback4="Correct, but there are other qualities you should look for. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | image= ""> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="4" | ||
| + | question="You have organized your blood transfusion and are now ready for surgery. Then you realize that you have forgotten to do something. What is it?" | ||
| + | choice1="Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspirate of the mass to determine if it is malignant or benign " | ||
| + | choice2="Activated clotting time" | ||
| + | choice3="Thoracic radiographs " | ||
| + | choice4="Bone marrow biopsy" | ||
| + | choice5="Activated clotting time and thoracic radiographs " | ||
| + | correctchoice="5" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. This is unlikely to be diagnostic, and even if it is, will not change the treatment, i.e. surgical resection, and may cause unnecessary bleeding. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback2="Correct. This is important to test if she is in disseminated intravascular coagulation, and as a reference for postoperative monitoring. It is also of use if the mass is of hepatic origin. However, you also need thoracic radiographs for staging purposes. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="Correct. You should take thoracic radiographs for staging purposes before surgery for any patient with an abdominal mass. The presence of pulmonary metastatic lesions may change the client’s willingness to treat. However, it would also be ideal to have an activated clotting time before surgery. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Incorrect'''. This is an unnecessary test for this dog. Choose again" | ||
| + | feedback5="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | image= ""> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Results | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Case 22 act.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | ! ||Anaesthetic considerations | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | a) ||Tilting the patient so that the head is slightly higher than the abdomen to allow the mass to fall away from the chest and enable adequate chest expansion | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | b) ||Blood pressure readings before, during and after surgery | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | c) ||Warming the patient intraoperatively as she is small and will become cold quickly | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | d) ||Ensuring intravenous fluid support and potentially the use of colloids for blood pressure support | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | e) ||Minimizing blood loss | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | f) ||Fast, efficient surgical technique | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="5" | ||
| + | question="You have your results for the in-house Activated clotting time and have confirmed that the thoracic radiographs were unremarkable. You are ready for surgery and about to anaesthetize the patient. What anaesthetic considerations run through your head? (Select from the table above.)]" | ||
| + | choice1="a, b, c, d, e, f" | ||
| + | choice2="a, b, d, f" | ||
| + | choice3="b, d, f" | ||
| + | choice4="c, d, e, f" | ||
| + | choice5="a, c, e" | ||
| + | correctchoice="1" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | feedback2="Correct, but there are other considerations. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="Correct, but there are other considerations. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback4="Correct, but there are other considerations. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="Correct, but there are other considerations. Choose again." | ||
| + | image= "File:Case 22 IMG 0004 1.JPG"> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="6" | ||
| + | question="You perform the surgery and fortunately it is a splenic mass rather than a huge liver mass. The mass is not ruptured and is removed via splenectomy. The abdomen is closed, she recovers remarkably well and is eating ravenously for the first time in months a few hours after surgery. What is the two-thirds rule of splenic masses?" | ||
| + | choice1="Two-thirds are benign and one-third are malignant. Haemangiosarcoma make up two-thirds of the malignant types " | ||
| + | choice2="Two-thirds are malignant and one-third are benign. Haemangiosarcoma make up one-third of the malignant types " | ||
| + | choice3="Two-thirds are malignant and one-third are benign. Haemangiosarcoma make up two-thirds of the malignant types " | ||
| + | choice4="Two-thirds are malignant and one-third are benign. Histiocytic tumours make up two-thirds of the malignant types " | ||
| + | choice5="" | ||
| + | correctchoice="3" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="" | ||
| + | image= "File:Case 22 IMG 0009.JPG"> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="7" | ||
| + | question="If this splenic mass was a haemangiosarcoma and had ruptured, what stage would it be and why?" | ||
| + | choice1="Stage I: whether the spleen is ruptured does not influence the staging " | ||
| + | choice2="Stage I, because the spleen has ruptured " | ||
| + | choice3="Stage II, because the spleen has ruptured " | ||
| + | choice4="Stage II, because it was very large " | ||
| + | choice5="Stage III, because it was very large" | ||
| + | correctchoice="3" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | image= "File:Case 22 IMG 0006.JPG"> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="8" | ||
| + | question="If the tumour was found at surgery to be a massive liver tumour (isolated to one lobe, usually low-grade hepatocellular carcinoma), what is the prognosis with complete surgical resection?" | ||
| + | choice1="One-year median survival time with 50% recurrence " | ||
| + | choice2="Two years’ median survival time with 10% recurrence " | ||
| + | choice3="Three years’ median survival time with 5% recurrence" | ||
choice4="" | choice4="" | ||
choice5="" | choice5="" | ||
| − | correctchoice=" | + | correctchoice="3" |
| − | feedback1="" | + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." |
| − | feedback2="" | + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." |
| − | feedback3="" | + | feedback3="'''Correct'''." |
feedback4="" | feedback4="" | ||
feedback5="" | feedback5="" | ||
| Line 106: | Line 207: | ||
<center><WikiQuiz | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| − | questionnumber="4" | + | questionnumber="9" |
| − | question="" | + | question="If the mass was found to be a massive liver tumour, what piece of surgical equipment could prove most invaluable?" |
| − | choice1="" | + | choice1="Thoracoabdominal (TA) surgical stapling device " |
| − | choice2="" | + | choice2="Electrocautery" |
| − | choice3="" | + | choice3="Haemostatic sponge (Gelfoam® or similar)" |
| + | choice4="Surgical suction " | ||
| + | choice5="" | ||
| + | correctchoice="1" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Correct'''. This is the most useful options, which can prove invaluable for liver lobectomies. It is also useful for lung lobectomies." | ||
| + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. This is useful for haemostasis, but not as useful as a surgical stapling device. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="'''Incorrect'''. This is useful for haemostasis, but not as useful as a surgical stapling device. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Incorrect'''. This is an essential tool for oncological abdominal surgery, but not as useful as a surgical stapling device. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="" | ||
| + | image= ""> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="10" | ||
| + | question="Your patient is now in recovery and sleeping well. Your client wants to take her home immediately. Why does this patient still need close monitoring and what piece of equipment is essential for this postoperative patient?" | ||
| + | choice1="Removal of such a large tumour will result in an internal seroma so she needs to be connected to a suction device to draw off excessive fluid from the abdomen" | ||
| + | choice2="Cardiac arrhythmias are common after splenic surgery and she should be connected to an electrocardiograph to monitor her heart" | ||
| + | choice3="A large splenic mass can cause compression of the lungs by squashing the diaphragm, making her hypoxic, so a blood gas is required every 4 hours after surgery " | ||
| + | choice4="A large splenic mass may result in compression of the urinary bladder and lead to acute renal failure. She needs an indwelling urinary catheter to monitor urine production" | ||
| + | choice5="" | ||
| + | correctchoice="2" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback2="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | feedback3="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="" | ||
| + | image= ""> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="11" | ||
| + | question="You monitor the electrocardiograph and notice she has developed a significant arrhythmia. What is the commonest arrhythmia seen in canine patients after splenic surgery?" | ||
| + | choice1="Atrial fibrillation " | ||
| + | choice2="Supraventricular tachycardia " | ||
| + | choice3="Increased vagal tone resulting in bradycardia " | ||
| + | choice4="Ventricular premature contractions " | ||
| + | choice5="Asystole" | ||
| + | correctchoice="4" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | feedback5="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | image= ""> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="12" | ||
| + | question="How would you manage your patient’s arrhythmia?" | ||
| + | choice1="Lidocaine" | ||
| + | choice2="Procainamide" | ||
| + | choice3="Beta-blocker" | ||
| + | choice4="Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor" | ||
| + | choice5="Pimobendan" | ||
| + | correctchoice="1" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. There is a better drug choice. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="'''Incorrect'''. You selected the wrong drug and your patient did not respond to treatment. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Incorrect'''. You selected the wrong drug and your patient did not respond to treatment. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="'''Incorrect'''. You selected the wrong drug and your patient did not respond to treatment. Choose again." | ||
| + | image= ""> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Histopathology Report | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Case 22 histopathology.jpg]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="13" | ||
| + | question="You send samples of the mass off to histopathology. Now that you have the results of histology, what do you do next?" | ||
| + | choice1="Advise she should receive adjuvant doxorubicin chemotherapy as the next step, to begin once the wound has healed. You also advise regular follow-ups for 12 months after surgery." | ||
| + | choice2="Offer nothing further as therapy and advise a recheck in 10−14 days for suture removal, then further rechecks every 3−6 months for 12 months after surgery." | ||
| + | choice3="Advise the clients that this kind of tumour is reported to occur infrequently as a splenic mass. However the prognosis is expected to be good with surgery alone, with a low metastatic rate. Adjuvant doxorubicin chemotherapy could be considered the more aggressive next step. This may be beneficial but data to prove this conclusively are lacking. A valid option is no further therapy as the surgery is potentially curative. Removing such a large abdominal mass is a strongly palliative option. Schedule a recheck in 10−14 days for suture removal, then further rechecks every 3−6 months for 12 months after surgery." | ||
choice4="" | choice4="" | ||
choice5="" | choice5="" | ||
| − | correctchoice=" | + | correctchoice="3" |
| − | feedback1="" | + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. You should discuss with the clients that chemotherapy may be of use to extend survival time, but this has not been proven. Strongly recommending adjuvant chemotherapy without sufficient data to support its benefit is controversial. Choose again." |
| − | feedback2="" | + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. There is insufficient evidence to exclude or include adjuvant chemotherapy as part of the treatment options for this kind of tumour. You should give the clients the option of considering adjuvant chemotherapy. Choose again." |
| − | feedback3="" | + | feedback3="'''Correct'''. This is the option that allows the clients to make their own decision knowing all the current information." |
feedback4="" | feedback4="" | ||
feedback5="" | feedback5="" | ||
| Line 123: | Line 298: | ||
<center><WikiQuiz | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| − | questionnumber=" | + | questionnumber="14" |
| − | question="" | + | question="With respect to other splenic masses seen in dogs, what do we understand by the term ‘nodular fibrohistiocytic proliferation’?" |
| − | choice1="" | + | choice1="This is another name for nodular hyperplasia " |
| − | choice2="" | + | choice2="These nodules have characteristics of splenic lymphoid hyperplasia and malignant splenic stromal tumours " |
| − | choice3="" | + | choice3="This is another name for histiocytic sarcoma " |
| − | choice4="" | + | choice4="These nodules are characterized by malignant lymphoid cells " |
| + | choice5="These nodules are characterized by high ratios of benign lymphoid cells and aggressive mesenchymal cells " | ||
| + | correctchoice="2" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback2="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | feedback3="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | image= ""> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="15" | ||
| + | question="Infiltrative disease of the spleen, e.g. lymphoma or metastatic mast cell tumour, can appear ultrasonographically like what non-neoplastic condition affecting the spleen?" | ||
| + | choice1="Extramedullary haematopoiesis " | ||
| + | choice2="Splenic infarct " | ||
| + | choice3="Splenic torsion " | ||
| + | choice4="Splenitis" | ||
choice5="" | choice5="" | ||
correctchoice="4" | correctchoice="4" | ||
| − | feedback1="" | + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." |
| − | feedback2="" | + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." |
| − | feedback3="" | + | feedback3="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." |
| − | feedback4="" | + | feedback4="'''Correct'''." |
feedback5="" | feedback5="" | ||
image= ""> | image= ""> | ||
</WikiQuiz></center> | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="16" | ||
| + | question="What are the most common tumours seen in the spleen of cats?" | ||
| + | choice1="Lymphoma: haemangiosarcoma " | ||
| + | choice2="Mast cell tumour: haemangiosarcoma " | ||
| + | choice3="Lymphoma: mast cell tumour " | ||
| + | choice4="Haemangiosarcoma: liposarcoma " | ||
| + | choice5="Histiocytic sarcoma: mast cell tumour " | ||
| + | correctchoice="3" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | image= ""> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><WikiQuiz | ||
| + | questionnumber="17" | ||
| + | question="In cats, what is the treatment of choice for splenic mast cell tumour and what is the prognosis with treatment?" | ||
| + | choice1="Splenectomy; poor prognosis" | ||
| + | choice2="Chemotherapy; poor prognosis " | ||
| + | choice3="Splenectomy; good prognosis " | ||
| + | choice4="Chemotherapy; good prognosis " | ||
| + | choice5="No treatment; grave prognosis" | ||
| + | correctchoice="3" | ||
| + | feedback1="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback2="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback3="'''Correct'''." | ||
| + | feedback4="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | feedback5="'''Incorrect'''. Choose again." | ||
| + | image= ""> | ||
| + | </WikiQuiz></center> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | {{Elsevier | ||
| + | |url = http://www.elsevierhealth.co.uk/product.jsp?isbn=9780702042508 | ||
| + | |book = North and Banks, Small Animal Oncology | ||
| + | |image = North and Banks SA Oncology.jpg | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Case-based Quizzes]] |
Latest revision as of 18:10, 4 October 2012
Signalment:
- 12-year-old female neutered Maltese Terrier cross
Presenting complaint:
- abdominal enlargement, lethargy, inappetance for 3 months. Your physical exam shows an obviously distended abdomen with a very large (>10 cm diameter) firm palpable abdominal mass, mucous membranes pink but paler than normal, periodontal disease. Otherwise clinical exam within normal limits, and she seems surprisingly alert and responsive. The clients say the abdominal enlargement has only happened in the past month.
1 |
What do you do next? |
| Abdominal ultrasound report |
|---|

|
| PCV and TP report |
|---|

|
| Urinalysis report |
|---|

|
2 |
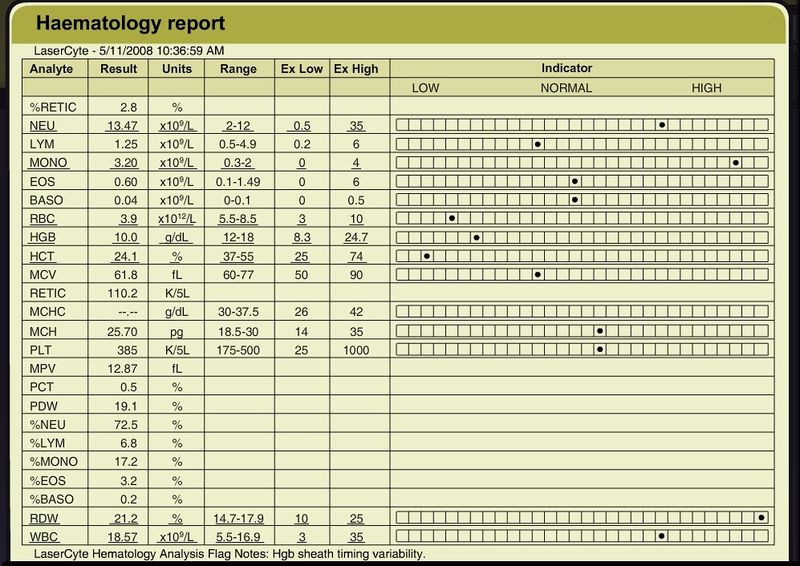
Review the abdominal ultrasound report, the packed cell volume and total protein report and the urinalysis report. What do you do next? |
| Haematology report |
|---|
|
| Serum biochemistry report |
|---|
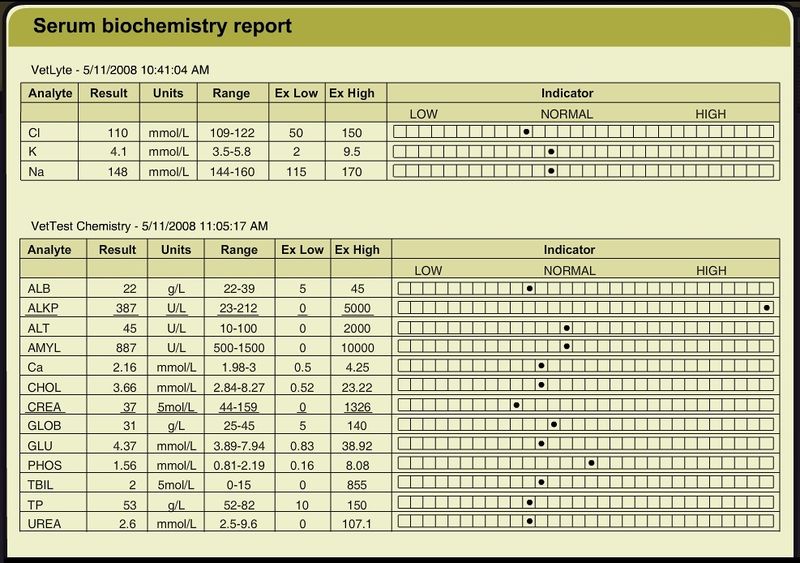
|
| Blood donor qualities | |
|---|---|
| a) | healthy, receives yearly physical exam, CBC, UA, biochemistry |
| b) | not been the recipient of a transfusion |
| c) | over 25kg |
| d) | negative for DEA1.1 |
| e) | fully vaccinated, heartworm negative, dogs receiving heartworm prophylaxis |
| f) | screened for Ehrlichia and Babesia (in areas where these occur |
3 |
Your next tests are haematology and serum biochemistry. You give the option of referral for surgery but the clients decline. You are not sure what to expect at surgery so you hire a suction unit and electrocautery unit from a drug company. You ask the clients to bring in their friend's dog so you have a whole blood transfusion on hand if needed. What qualities should you look for in choosing a blood donor for your surgical patient? (Select from the table above.) |
4 |
You have organized your blood transfusion and are now ready for surgery. Then you realize that you have forgotten to do something. What is it? |
| Results |
|---|

|
| Anaesthetic considerations | |
|---|---|
| a) | Tilting the patient so that the head is slightly higher than the abdomen to allow the mass to fall away from the chest and enable adequate chest expansion |
| b) | Blood pressure readings before, during and after surgery |
| c) | Warming the patient intraoperatively as she is small and will become cold quickly |
| d) | Ensuring intravenous fluid support and potentially the use of colloids for blood pressure support |
| e) | Minimizing blood loss |
| f) | Fast, efficient surgical technique |
5 |
You have your results for the in-house Activated clotting time and have confirmed that the thoracic radiographs were unremarkable. You are ready for surgery and about to anaesthetize the patient. What anaesthetic considerations run through your head? (Select from the table above.)] |
6 |
You perform the surgery and fortunately it is a splenic mass rather than a huge liver mass. The mass is not ruptured and is removed via splenectomy. The abdomen is closed, she recovers remarkably well and is eating ravenously for the first time in months a few hours after surgery. What is the two-thirds rule of splenic masses? |
7 |
If this splenic mass was a haemangiosarcoma and had ruptured, what stage would it be and why? |
8 |
If the tumour was found at surgery to be a massive liver tumour (isolated to one lobe, usually low-grade hepatocellular carcinoma), what is the prognosis with complete surgical resection? |
9 |
If the mass was found to be a massive liver tumour, what piece of surgical equipment could prove most invaluable? |
10 |
Your patient is now in recovery and sleeping well. Your client wants to take her home immediately. Why does this patient still need close monitoring and what piece of equipment is essential for this postoperative patient? |
11 |
You monitor the electrocardiograph and notice she has developed a significant arrhythmia. What is the commonest arrhythmia seen in canine patients after splenic surgery? |
12 |
How would you manage your patient’s arrhythmia? |
| Histopathology Report |
|---|

|
13 |
You send samples of the mass off to histopathology. Now that you have the results of histology, what do you do next? |
14 |
With respect to other splenic masses seen in dogs, what do we understand by the term ‘nodular fibrohistiocytic proliferation’? |
15 |
Infiltrative disease of the spleen, e.g. lymphoma or metastatic mast cell tumour, can appear ultrasonographically like what non-neoplastic condition affecting the spleen? |
16 |
What are the most common tumours seen in the spleen of cats? |
17 |
In cats, what is the treatment of choice for splenic mast cell tumour and what is the prognosis with treatment? |
| This resource was adapted from North and Banks, Small Animal Oncology provided by Elsevier Health Sciences as part of the PublishOER Project. | 
|