Difference between revisions of "Pulex irritans"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{unfinished}} | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Pulex irritans.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Pulex irritans''' <br> Zsoldos Márton 2004, Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Pulex irritans.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Pulex irritans''' <br> Zsoldos Márton 2004, Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| Line 7: | Line 9: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | = | + | {{Taxobox |
| − | + | |name =''Pulex irritans | |
| − | + | |kingdom = | |
| − | | | + | |phylum = |
| − | | Insecta | + | |class =[[Insecta]] |
| − | |- | + | |sub-class = |
| − | | | + | |order =[[Siphonaptera]] |
| − | | | + | |super-family = |
| − | |- | + | |family = Pulicidae |
| − | | | + | |sub-family = |
| − | | | + | |genus = |
| − | + | |species = | |
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | ==Hosts== | |
| + | Humans and pigs. | ||
| − | + | ==Identification== | |
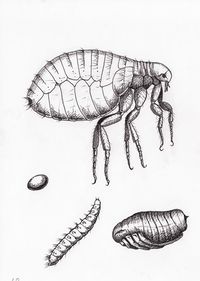
| + | ''P. irritans is a flea of the class [[Insecta]]. There are no genal, or pronotal ctenidia. | ||
| − | + | ==Life Cycle== | |
| + | The egss are laid in the host faeces. The eggs then hatch, and undergo three larval stages. The larvae then pupate before becoming adults. | ||
See [[Flea Life Cycle|general flea life cycle]]. | See [[Flea Life Cycle|general flea life cycle]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 29 July 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
| Also known as: | Human flea |
| Pulex irritans | |
|---|---|
| Class | Insecta |
| Order | Siphonaptera |
| Family | Pulicidae |
Hosts
Humans and pigs.
Identification
P. irritans is a flea of the class Insecta. There are no genal, or pronotal ctenidia.
Life Cycle
The egss are laid in the host faeces. The eggs then hatch, and undergo three larval stages. The larvae then pupate before becoming adults.