Difference between revisions of "Rabbit Medicine and Surgery Q&A 10"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Template:Manson Keeble Meredith}} centre|500px <br /> '''An adult female entire Netherland Dwarf rabbit presents with fur pulling involving ...") |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|a1= | |a1= | ||
Fur pulling in entire female rabbits, without a history of contact with an entire male, is likely to be associated with pseudopregnancy. | Fur pulling in entire female rabbits, without a history of contact with an entire male, is likely to be associated with pseudopregnancy. | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1=Pseudopregnancy - Rabbit |
|q2=What other clinical signs may be associated with this problem in does? | |q2=What other clinical signs may be associated with this problem in does? | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
*increased aggression. <br><br> | *increased aggression. <br><br> | ||
The condition lasts for approximately 16–18 days, during which time the doe will not let herself be mounted. Mammary hyperplasia may lead to mastitis. If prolonged or recurrent, this condition may develop into hydrometra or pyometra. | The condition lasts for approximately 16–18 days, during which time the doe will not let herself be mounted. Mammary hyperplasia may lead to mastitis. If prolonged or recurrent, this condition may develop into hydrometra or pyometra. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2=Pseudopregnancy - Rabbit |
|q3=Why does this condition occur in the rabbit? | |q3=Why does this condition occur in the rabbit? | ||
|a3= Pseudopregnancy in does occurs as a direct result of normal elevations in plasma prolactin concentration post ovulation. This may occur following a sterile or unsuccessful mating (rabbits are induced ovulators) or following ovulation stimulated by mounting of another doe. | |a3= Pseudopregnancy in does occurs as a direct result of normal elevations in plasma prolactin concentration post ovulation. This may occur following a sterile or unsuccessful mating (rabbits are induced ovulators) or following ovulation stimulated by mounting of another doe. | ||
| − | |l3= | + | |l3=Pseudopregnancy - Rabbit |
|q4=What are the treatment options available? | |q4=What are the treatment options available? | ||
|a4= | |a4= | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*Ovariohysterectomy is indicated for long-term prevention. | *Ovariohysterectomy is indicated for long-term prevention. | ||
*In chronic cases the use of cabergoline (5 μg/kg q24h for 4–6 days) has been anecdotally reported as being effective in the treatment of persistent lactation in does. (NB: This drug is not licensed in rabbits and its side-effects and therapeutic actions are not known.) | *In chronic cases the use of cabergoline (5 μg/kg q24h for 4–6 days) has been anecdotally reported as being effective in the treatment of persistent lactation in does. (NB: This drug is not licensed in rabbits and its side-effects and therapeutic actions are not known.) | ||
| − | |l4= | + | |l4=Pseudopregnancy - Rabbit#Treatment |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:52, 11 August 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Rabbit Medicine and Surgery questions |
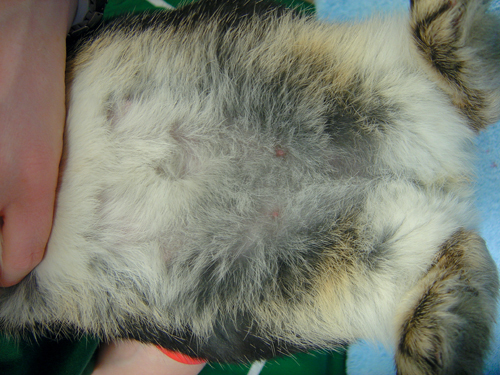
An adult female entire Netherland Dwarf rabbit presents with fur pulling involving the ventral abdomen. The animal is housed indoors with another female rabbit.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is the likely underlying condition? | Fur pulling in entire female rabbits, without a history of contact with an entire male, is likely to be associated with pseudopregnancy. |
Link to Article | |
| What other clinical signs may be associated with this problem in does? | Other clinical signs that may be present include
The condition lasts for approximately 16–18 days, during which time the doe will not let herself be mounted. Mammary hyperplasia may lead to mastitis. If prolonged or recurrent, this condition may develop into hydrometra or pyometra. |
Link to Article | |
| Why does this condition occur in the rabbit? | Pseudopregnancy in does occurs as a direct result of normal elevations in plasma prolactin concentration post ovulation. This may occur following a sterile or unsuccessful mating (rabbits are induced ovulators) or following ovulation stimulated by mounting of another doe.
|
Link to Article | |
| What are the treatment options available? |
|
Link to Article | |