Difference between revisions of "Small Animal Soft Tissue Surgery Q&A 01"
(Created page with "[[|centre|500px]] <br /> '''This dog was presented with an acute inability to close the mouth but no lateral deviation of the mandible.''' <br /> <FlashCard questions="3"> |q...") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[|centre|500px]] | + | {{Template:Manson |
| + | |book = Small Animal Soft Tissue Surgery Q&A}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:SmAn ST Sx 01.jpg|centre|500px]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
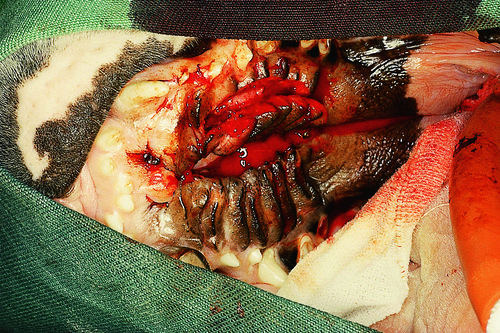
| − | ''' | + | '''A surgical procedure underway in the oral cavity of a four-month-old, male Bulldog is shown. The owner’s complaint is that the dog has a chronic mucopurulent nasal discharge, coughs when eating or drinking, and has not been gaining weight at a rate equal to that of his litter mates. He also has a foul odor from the oral cavity.''' |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<FlashCard questions="3"> | <FlashCard questions="3"> | ||
| − | |q1=What is | + | |q1=What is the diagnosis? |
|a1= | |a1= | ||
| − | + | Congenital cleft of the hard and soft palates (secondary palatal defect). | |
| − | |l1= | + | |l1=Cleft Palate |
| − | |q2= | + | |q2=What secondary complication may be associated with this defect? |
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| − | + | Aspiration pneumonia is often a complication of secondary palate defects. The animal should be evaluated with thoracic radiographs and treated appropriately prior to surgical correction of the palate defect. | |
| − | + | |l2=Cleft Palate | |
| − | + | |q3=What are three principles to be followed during surgical repair of this problem? | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |l2= | ||
| − | |q3= | ||
|a3= | |a3= | ||
| − | + | Repair flaps should be larger than the primary defect to reduce tension on suture lines. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Connective tissue and vascular supply is preserved by limited meticulous dissection (avoid the palatine artery) and gentle tissue handling. | |
| − | + | Tissue flaps are apposed to cleanly incised epithelium to ensure healing. | |
| − | |l3= | + | Temporary feeding via a pharyngostomy or gastrostomy tube should be considered to bypass the oral cavity during wound healing. |
| + | |l3=Cleft Palate#Treatment | ||
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:09, 19 October 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Small Animal Soft Tissue Surgery Q&A. |
A surgical procedure underway in the oral cavity of a four-month-old, male Bulldog is shown. The owner’s complaint is that the dog has a chronic mucopurulent nasal discharge, coughs when eating or drinking, and has not been gaining weight at a rate equal to that of his litter mates. He also has a foul odor from the oral cavity.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is the diagnosis? | Congenital cleft of the hard and soft palates (secondary palatal defect). |
Link to Article | |
| What secondary complication may be associated with this defect? | Aspiration pneumonia is often a complication of secondary palate defects. The animal should be evaluated with thoracic radiographs and treated appropriately prior to surgical correction of the palate defect. |
Link to Article | |
| What are three principles to be followed during surgical repair of this problem? | Repair flaps should be larger than the primary defect to reduce tension on suture lines. Connective tissue and vascular supply is preserved by limited meticulous dissection (avoid the palatine artery) and gentle tissue handling. Tissue flaps are apposed to cleanly incised epithelium to ensure healing. Temporary feeding via a pharyngostomy or gastrostomy tube should be considered to bypass the oral cavity during wound healing. |
Link to Article | |