Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction
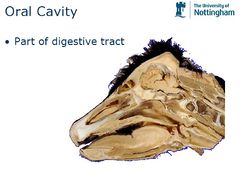
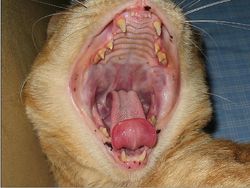
The oral cavity is the first section of the alimentary tract that receives food. It provides the digestive functions of prehension, mastication and in salivation and also plays a role in the respiratory system through oral breathing when the nasopharynx is impaired. The oral cavity or mouth, consists of accessory structures (the salivary glands), projecting structures, (the teeth and the tongue) and the walls enclosing the oral cavity.
Anatomical Boundaries
The oral cavity is bordered rostrally by the lips and caudally by the pharynx at the level of the palatoglossal arches.
Outer Vestibule
The teeth and jaw margins medially and the lips and cheeks laterally. The ramus of the mandible and masseter muscle caudally.
Oral Cavity Proper
Inside the dental arches, the palate borders dorsally and the teeth, gums and jaw margins laterally. The tongue margins ventrally. The size can be altered by raising or lowering the tongue and the floor of the oral cavity when the mouth is closed.
Origin and Innervation
The oral cavity originates from ectoderm. It is innervated by the trigeminal nerve (CN V).
| Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Oral Cavity anatomy Oral Cavity pathology |
 Selection of relevant PowerPoint tutorials |
Histology tutorials about the oral cavity |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/dentistry/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS