Difference between revisions of "Nasal Cavity Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | # | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
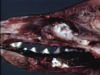
| + | [[Image:Nasal cavity carcinoma.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Nasal cavity carcinoma (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Nasal neoplasia in general=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Majority are malignant, locally invasive but do not metastasise | ||
| + | *Usually pale, soft, fleshy or friable | ||
| + | *May be [[Bones Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology|osteoma or osteosarcoma, chondroma or chondrosarcoma]], fibroma or fibrosarcoma, myxoma or myxosarcoma, haemangioma or haemangiosarcoma, adenoma or adenocarcinoma | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Adenocarcinoma=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Transitional Cell Carcinoma]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Squamous cell carcinoma=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In cats they arise mainly from nasal vestibule | ||
| + | *In horses they originate mainly from maxillary sinus | ||
| + | *Most common nasal tumour | ||
| + | **Serosanquineous or mucopurulent, odourous nasal discharge | ||
| + | *Tissue necrosis | ||
| + | *May cause airway obstruction or facial distortion | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology]] | ||
| + | ===Olfactory neuroblastoma=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Rare, mainly occurs in cats | ||
| + | *Arises from ethmoturbinates in caudal region of nasal cavity | ||
| + | *May penetrate cribriform plate into cerebral cortex | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology]] | ||
| + | ===Ethmoturbinate tumours (papillomas and adenocarcinomas)=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In horses and other species | ||
| + | *Multiple species may be affected on one premises | ||
| + | *Arising from olfactory cells are endemic in some parts of the world for unknown reason | ||
| + | *May be caused by a virus? | ||
| + | [[Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Progressive ethmoidal haematoma=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Slowly expanding non-neoplastic mass of horses | ||
| + | *Originates from submucosa of ethmoidal labyrinth | ||
| + | *Either from nasal or sinusal portion of ethmoid labyrinth | ||
| + | *Unilateral, can extend to nostrils or choanae | ||
| + | *Rarely elsewhere in sinuses | ||
| + | *Expands to nasal cavity, [[Paranasal Sinuses Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology|paranasal sinuses]], [[Nasopharynx Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology|nasopharynx]] causing destruction of tissue | ||
| + | *Micro - haemorrhage, calcification of connective tissue fibres | ||
| + | *[[Aspergillus spp.|''Aspergillus'' spp.]] may be present on the lesion | ||
| + | *May cause [[Respiratory System Clinical Signs - Pathology#Epistaxis|epistaxis]] | ||
| + | *Can recur after surgical excision | ||
| + | *May arise subsequently to [[Rhinitis#Chronic rhinitis|chronic inflammation]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology]] | ||
| + | ===Nasal polyps=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Polypoid thickening of the inflamed nasal musosa, hyperplastic epithelium | ||
| + | *Pinkish, often pedunculated masses, round, often large and multiple proturberences into the nasal meatus | ||
| + | *Can arise subsequently to [[Rhinitis#Chronic rhinitis|chronic inflammation]] | ||
| + | *Old polyps may becoma fibrous | ||
| + | *May recur when excised | ||
| + | *Necessary to distinguish from neoplasia | ||
| + | *Common in cats, less often in dogs, also horses and sheep | ||
| + | *Also see [[Nasal Cavity Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology#Progressive ethmoidal haematoma|Progressive haematoma]] of horses and [[Nasopharynx Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology#Nasopharyngeal polyps of cats|Nasopharyngeal polyps]] of cats | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology]] | ||
| + | ===Nasal and paranasal sinus cysts=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Mimic infection or neoplasms | ||
| + | *Expand and destroy surrounding tissue | ||
| + | *Epithelial capsule with haemorrhagic or yellow fluid | ||
| + | *Do not tend to recur after surgery | ||
| + | [[Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Test yourself with the Nasal Cavity Pathology Flashcards== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Nasal_Cavity_Flashcards_-_Pathology|Nasal Cavity Pathology Flashcards]] | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 15 February 2011
Nasal neoplasia in general
- Majority are malignant, locally invasive but do not metastasise
- Usually pale, soft, fleshy or friable
- May be osteoma or osteosarcoma, chondroma or chondrosarcoma, fibroma or fibrosarcoma, myxoma or myxosarcoma, haemangioma or haemangiosarcoma, adenoma or adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
- In cats they arise mainly from nasal vestibule
- In horses they originate mainly from maxillary sinus
- Most common nasal tumour
- Serosanquineous or mucopurulent, odourous nasal discharge
- Tissue necrosis
- May cause airway obstruction or facial distortion
Olfactory neuroblastoma
- Rare, mainly occurs in cats
- Arises from ethmoturbinates in caudal region of nasal cavity
- May penetrate cribriform plate into cerebral cortex
Ethmoturbinate tumours (papillomas and adenocarcinomas)
- In horses and other species
- Multiple species may be affected on one premises
- Arising from olfactory cells are endemic in some parts of the world for unknown reason
- May be caused by a virus?
Progressive ethmoidal haematoma
- Slowly expanding non-neoplastic mass of horses
- Originates from submucosa of ethmoidal labyrinth
- Either from nasal or sinusal portion of ethmoid labyrinth
- Unilateral, can extend to nostrils or choanae
- Rarely elsewhere in sinuses
- Expands to nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx causing destruction of tissue
- Micro - haemorrhage, calcification of connective tissue fibres
- Aspergillus spp. may be present on the lesion
- May cause epistaxis
- Can recur after surgical excision
- May arise subsequently to chronic inflammation
Nasal polyps
- Polypoid thickening of the inflamed nasal musosa, hyperplastic epithelium
- Pinkish, often pedunculated masses, round, often large and multiple proturberences into the nasal meatus
- Can arise subsequently to chronic inflammation
- Old polyps may becoma fibrous
- May recur when excised
- Necessary to distinguish from neoplasia
- Common in cats, less often in dogs, also horses and sheep
- Also see Progressive haematoma of horses and Nasopharyngeal polyps of cats
Nasal and paranasal sinus cysts
- Mimic infection or neoplasms
- Expand and destroy surrounding tissue
- Epithelial capsule with haemorrhagic or yellow fluid
- Do not tend to recur after surgery