Difference between revisions of "Nasal Cavity Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
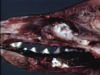
| − | # | + | [[Image:Nasal cavity carcinoma.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Nasal cavity carcinoma (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Nasal neoplasia in general=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Majority are malignant, locally invasive but do not metastasise | ||
| + | *Usually pale, soft, fleshy or friable | ||
| + | *May be [[Bones Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology|osteoma or osteosarcoma, chondroma or chondrosarcoma]], fibroma or fibrosarcoma, myxoma or myxosarcoma, haemangioma or haemangiosarcoma, adenoma or adenocarcinoma | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Adenocarcinoma=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Transitional Cell Carcinoma]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Squamous cell carcinoma=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Olfactory Neuroblastoma]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Ethmoturbinate Tumours]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Progressive Ethmoidal Haematoma]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Nasal polyps=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Polypoid thickening of the inflamed nasal musosa, hyperplastic epithelium | ||
| + | *Pinkish, often pedunculated masses, round, often large and multiple proturberences into the nasal meatus | ||
| + | *Can arise subsequently to [[Rhinitis#Chronic rhinitis|chronic inflammation]] | ||
| + | *Old polyps may becoma fibrous | ||
| + | *May recur when excised | ||
| + | *Necessary to distinguish from neoplasia | ||
| + | *Common in cats, less often in dogs, also horses and sheep | ||
| + | *Also see [[Nasal Cavity Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology#Progressive ethmoidal haematoma|Progressive haematoma]] of horses and [[Nasopharynx Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology#Nasopharyngeal polyps of cats|Nasopharyngeal polyps]] of cats | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology]] | ||
| + | ===Nasal and paranasal sinus cysts=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Mimic infection or neoplasms | ||
| + | *Expand and destroy surrounding tissue | ||
| + | *Epithelial capsule with haemorrhagic or yellow fluid | ||
| + | *Do not tend to recur after surgery | ||
| + | [[Category:Nasal Cavity - Hyperplastic/Neoplastic Pathology]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Test yourself with the Nasal Cavity Pathology Flashcards== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Nasal_Cavity_Flashcards_-_Pathology|Nasal Cavity Pathology Flashcards]] | ||
Revision as of 18:04, 15 February 2011
Nasal neoplasia in general
- Majority are malignant, locally invasive but do not metastasise
- Usually pale, soft, fleshy or friable
- May be osteoma or osteosarcoma, chondroma or chondrosarcoma, fibroma or fibrosarcoma, myxoma or myxosarcoma, haemangioma or haemangiosarcoma, adenoma or adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Olfactory Neuroblastoma
Progressive Ethmoidal Haematoma
Nasal polyps
- Polypoid thickening of the inflamed nasal musosa, hyperplastic epithelium
- Pinkish, often pedunculated masses, round, often large and multiple proturberences into the nasal meatus
- Can arise subsequently to chronic inflammation
- Old polyps may becoma fibrous
- May recur when excised
- Necessary to distinguish from neoplasia
- Common in cats, less often in dogs, also horses and sheep
- Also see Progressive haematoma of horses and Nasopharyngeal polyps of cats
Nasal and paranasal sinus cysts
- Mimic infection or neoplasms
- Expand and destroy surrounding tissue
- Epithelial capsule with haemorrhagic or yellow fluid
- Do not tend to recur after surgery