Difference between revisions of "Cheyletiella spp."
(Redirected page to Cheyletiellosis) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | # | + | {{Taxobox |
| + | |name =''Cheyletiella'' | ||
| + | |phylum =Arthropoda | ||
| + | |class =Arachnida | ||
| + | |subclass =Acari | ||
| + | |order =Trombidiformes | ||
| + | |family =Cheyletidae | ||
| + | |genus =Cheyletiella | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | [[Image:cheyletiella.jpg|thumb|right|200px|''Cheyletiella mite'' - Kalumet 2004,Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | [[Image:cheyletiella 2.jpg|thumb|right|200px|''Cheyletiella mite closeup'' - Kalumet 2004,Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cheyletiella mites are [[Non-Burrowing Mites|surface mites]] of dogs and cats. | ||
| + | They are also found on humans and rabbits. They cause [[Cheyletiellosis|Cheyletiellosis]], a parasitic skin infestation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Identification== | ||
| + | |||
| + | They have a waisted body and claw like palps on their heads. They also have combs at the ends of their legs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Lifecycle== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The lifecycle of a Cheyletiella mite lasts 21-35 days on the host. The adults mites can survive off the host for 2-14 days. They live on the skin surface and their eggs are attached to hair shafts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Pathogenesis== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The mites are highly contagious and cause mild pathogenesis. They are seen to cause very scaly dermatitis. Cheyletiella mites can be transferred to humans. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Important Species== | ||
| + | ''C.yasguri''- Most commonly found on dogs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''C.blakei''- Most commonly found on cats and humans. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''C.parasitivorax''- Most commonly [[Mites - Rabbit#Cheyletiella parasitivorax|found on rabbits]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Mites_Flashcards|Mites Flashcards]]<br>[[Small Mammals Q&A 13]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Taylor, M.A, Coop, R.L., Wall,R.L. (2007) '''Veterinary Parasitology''' ''Blackwell Publishing'' | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Non-Burrowing_Mites]][[Category:Cat Parasites]][[Category:Dog Parasites]][[Category:Rabbit Parasites]] | [[Category:Non-Burrowing_Mites]][[Category:Cat Parasites]][[Category:Dog Parasites]][[Category:Rabbit Parasites]] | ||
| + | [[Category:To_Do_-_Parasites]][[Category:To Do - Major]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Zoonoses]] | ||
Revision as of 14:47, 16 August 2011
| Cheyletiella | |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Arthropoda |
| Class | Arachnida |
| Order | Trombidiformes |
| Family | Cheyletidae |
| Genus | Cheyletiella |
Introduction
Cheyletiella mites are surface mites of dogs and cats. They are also found on humans and rabbits. They cause Cheyletiellosis, a parasitic skin infestation.
Identification
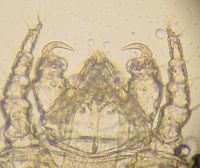
They have a waisted body and claw like palps on their heads. They also have combs at the ends of their legs.
Lifecycle
The lifecycle of a Cheyletiella mite lasts 21-35 days on the host. The adults mites can survive off the host for 2-14 days. They live on the skin surface and their eggs are attached to hair shafts.
Pathogenesis
The mites are highly contagious and cause mild pathogenesis. They are seen to cause very scaly dermatitis. Cheyletiella mites can be transferred to humans.
Important Species
C.yasguri- Most commonly found on dogs.
C.blakei- Most commonly found on cats and humans.
C.parasitivorax- Most commonly found on rabbits.
| Cheyletiella spp. Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Mites Flashcards Small Mammals Q&A 13 |
References
Taylor, M.A, Coop, R.L., Wall,R.L. (2007) Veterinary Parasitology Blackwell Publishing