Difference between revisions of "Small Animal Soft Tissue Surgery Q&A 18"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:Soft Tissue Sx 18a.jpg|centre|500px]] | [[Image:Soft Tissue Sx 18a.jpg|centre|500px]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 11: | ||
|a1= | |a1= | ||
Cholelithiasis | Cholelithiasis | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1= |
|q2=This disease is often insidious and asymptomatic in dogs. List the most common clinical signs in dogs that are symptomatic. | |q2=This disease is often insidious and asymptomatic in dogs. List the most common clinical signs in dogs that are symptomatic. | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
Vomiting, anorexia, weakness, polyuria/polydypsia, weight loss, icterus, fever and signs of abdominal pain are the most common clinical signs in dogs with symptomatic cholelithiasis. | Vomiting, anorexia, weakness, polyuria/polydypsia, weight loss, icterus, fever and signs of abdominal pain are the most common clinical signs in dogs with symptomatic cholelithiasis. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2= |
|q3=The pathogenesis of this disease in dogs is unknown. Several causes have been proposed. Name the most likely ones. | |q3=The pathogenesis of this disease in dogs is unknown. Several causes have been proposed. Name the most likely ones. | ||
|a3= | |a3= | ||
Proposed causes include trauma, biliary stasis, diet alterations, cholecystitis, and parasitic and bacterial biliary infection. | Proposed causes include trauma, biliary stasis, diet alterations, cholecystitis, and parasitic and bacterial biliary infection. | ||
| − | |l3= | + | |l3= |
|q4=Describe the surgical therapeutic options, and give the therapy of choice. | |q4=Describe the surgical therapeutic options, and give the therapy of choice. | ||
|a4= | |a4= | ||
| Line 29: | Line 25: | ||
Cholecystectomy is indicated in dogs with cholelithiasis and concurrent cholecystitis and should be regarded as therapy of choice. | Cholecystectomy is indicated in dogs with cholelithiasis and concurrent cholecystitis and should be regarded as therapy of choice. | ||
| − | |l4= | + | |l4= |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Revision as of 13:53, 30 August 2011
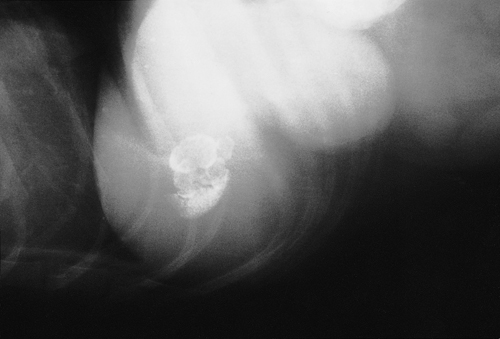
A right lateral radiograph of the cranial abdomen of a ten-year-old, female Schnauzer is shown.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is the diagnosis? | Cholelithiasis |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| This disease is often insidious and asymptomatic in dogs. List the most common clinical signs in dogs that are symptomatic. | Vomiting, anorexia, weakness, polyuria/polydypsia, weight loss, icterus, fever and signs of abdominal pain are the most common clinical signs in dogs with symptomatic cholelithiasis. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| The pathogenesis of this disease in dogs is unknown. Several causes have been proposed. Name the most likely ones. | Proposed causes include trauma, biliary stasis, diet alterations, cholecystitis, and parasitic and bacterial biliary infection. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| Describe the surgical therapeutic options, and give the therapy of choice. | The treatment for cholelithiasis is cholelithotomy via cholecystotomy, cholecystectomy or choledochotomy. Cholecystectomy is indicated in dogs with cholelithiasis and concurrent cholecystitis and should be regarded as therapy of choice. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |