Difference between revisions of "Micturition - Anatomy & Physiology"
| (13 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | + | ==Introduction== | |
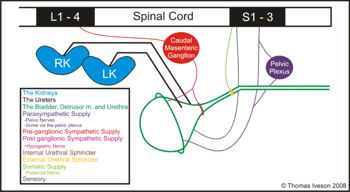
| − | | | + | [[Image:sumlutshcemtri.jpg|right|thumb|350px|<small><center>A schematic overview of the lower urinary tract showing the nerves and muscles involved in micturition</center></small>]] |
| − | | | + | '''Micturition is the normal process of the passive storage and active voiding of urine.''' |
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | Micturition is the normal process of the passive storage and active voiding of urine. | ||
| − | + | After entering the renal pelvis the modification of the urine is over in all domestic species other than the horse where mucin is added. The urine passes along the [[Ureters - Anatomy & Physiology| ureters]] and enters the [[Urinary Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology|bladder]]. It is here that the urine is stored until it is to be voided. Urine is not constantly excreted and it is only when there is a significant amount present in the bladder that the process of voiding occurs. Both the [[Urinary Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology| Bladder]] and the [[Urethra - Anatomy & Physiology| Urethra]] have smooth muscle and thus receive autonomic influence with regard to their activity. However the urethra also has an element of skeletal muscle giving the animal some degree of conscious control over the voiding of urine. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | After entering the renal pelvis the modification of the urine is over in all domestic species other than the horse where mucin is added. The urine passes along the [[Ureters - Anatomy & Physiology| ureters]] and enters the [[Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology|bladder]]. It is here that the urine is stored until it is to be voided. Urine is not constantly excreted and it is only when there is a significant amount present in the bladder that the process of voiding occurs. Both the [[Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology| Bladder]] and the [[Urethra - Anatomy & Physiology| Urethra]] have smooth muscle and thus receive autonomic influence with regard to their activity. However the urethra also has an element of skeletal muscle giving the animal some degree of conscious control over the voiding of urine. | ||
===Sensory Innervation=== | ===Sensory Innervation=== | ||
| − | |||
The bladder has stretch receptors (alpha receptors in the neck and trigone, and beta receptors in the body) which detect fullness of the bladder. These impulse to the pelvic nerves and so to the sacral spinal cord. The urethra has afferents detecting flow, distension and pain that go via the pudendal nerve to the sacral cord. | The bladder has stretch receptors (alpha receptors in the neck and trigone, and beta receptors in the body) which detect fullness of the bladder. These impulse to the pelvic nerves and so to the sacral spinal cord. The urethra has afferents detecting flow, distension and pain that go via the pudendal nerve to the sacral cord. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 13: | ||
===The Muscles=== | ===The Muscles=== | ||
| − | The motor components of the reflex are the [[Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology #Detrusor Muscle| Detrusor Muscle]], [[Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology #Internal Urethral Sphincter| Internal Urethral Sphincter]] and the [[Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology #External Urethral Sphincter| External Urethral Sphincter]]. The former two are supplied by the autonomic nervous system with the latter being of somatic innervation. | + | The motor components of the reflex are the [[Urinary Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology#Detrusor Muscle| Detrusor Muscle]], [[Urinary Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology#Internal Urethral Sphincter| Internal Urethral Sphincter]] and the [[Urinary Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology#External Urethral Sphincter| External Urethral Sphincter]]. The former two are supplied by the autonomic nervous system with the latter being of somatic innervation. |
==The Reflex== | ==The Reflex== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 37: | ||
This co-ordinated detrusor contraction and sphincter relaxation leads to complete voiding of the bladder and at the same time prevents pressure build up with in the bladder. | This co-ordinated detrusor contraction and sphincter relaxation leads to complete voiding of the bladder and at the same time prevents pressure build up with in the bladder. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[The Process of Micturition - Renal Flash Cards - Anatomy & Physiology|Micturition Flashcards]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Lower Urinary Tract - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:39, 5 July 2012
Introduction
Micturition is the normal process of the passive storage and active voiding of urine.
After entering the renal pelvis the modification of the urine is over in all domestic species other than the horse where mucin is added. The urine passes along the ureters and enters the bladder. It is here that the urine is stored until it is to be voided. Urine is not constantly excreted and it is only when there is a significant amount present in the bladder that the process of voiding occurs. Both the Bladder and the Urethra have smooth muscle and thus receive autonomic influence with regard to their activity. However the urethra also has an element of skeletal muscle giving the animal some degree of conscious control over the voiding of urine.
Sensory Innervation
The bladder has stretch receptors (alpha receptors in the neck and trigone, and beta receptors in the body) which detect fullness of the bladder. These impulse to the pelvic nerves and so to the sacral spinal cord. The urethra has afferents detecting flow, distension and pain that go via the pudendal nerve to the sacral cord.
Central Intregration
The co-ordination of the urethralis and detrusor muscles from information recieved from the stretch receptors occurs in the pons. This micturition centre also branches to the thalamus, cerebellum and cerebral cortex. It is the cerebral cortex that is responsible for voluntary control of micturition.
The Muscles
The motor components of the reflex are the Detrusor Muscle, Internal Urethral Sphincter and the External Urethral Sphincter. The former two are supplied by the autonomic nervous system with the latter being of somatic innervation.
The Reflex
Storage phase - Sympathetic system dominant
- This involves contraction of the urethral sphincters to prevent leakage of urine
- Alpha-adenergic stimulation causes constriction of the bladder neck
- Beta-adenergic stimulation causes relaxation of the detrusor muscle and so promotes low pressure filling of the bladder
- Direct inhibition of the pelvic nerves is provided by the hypogastric nerve
- The main barrier to urine outflow though is the constriction of the urethralis muscle being provided with constant tone by the pudendal nerve.
Once bladder capacity is reached the stretch receptors are stimulated which send impulses via the pelvic nerve to the sacral spinal cord and finally to the pons. Here integration occurs and there is concious acknowledgement of the need to urinate.
Emptying phase - Parasympathetic system dominant
The efferent impulses from the pons travel to the sacral region and simultaneously:
- Inhibition of the pudendal nerve, thus causing relaxation of the urethralis muscle.
- Stimulation of the parasymphathetic neurons, inhibiting adrenergic tone to the neck thus leading to relaxation of the internal urethral sphincter. This increased input also leads to contraction of the detrusor muscle.
This co-ordinated detrusor contraction and sphincter relaxation leads to complete voiding of the bladder and at the same time prevents pressure build up with in the bladder.
| Micturition - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Micturition Flashcards |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a7146892eab2_67883959 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a714689ee091_63033120 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a71468a8f1d8_31353763
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |