|
|
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | ==Instruments Used to Examine the Mouth== | + | {{Navigation2 |
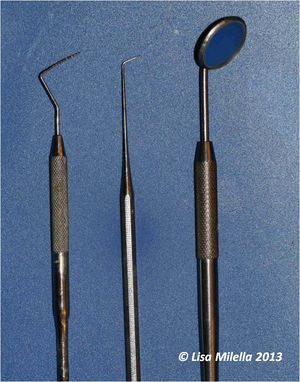
| − | [[File:Oral examination instruments.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Instruments used for oral examination – periodontal probe, explorer probe, dental mirror<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]] | + | |title = Small Animal Oral Examination Instruments |
| − | [[File:Explorer probes.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Different examples of explorer probes<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]]
| + | |categories = [[:Category:Dentistry|'''Dentistry''']] |
| − | ===Periodontal Probe=== | + | |text = |
| − | | + | |content = |
| − | The periodontal probe is a narrow rounded or flat, blunt-ended, graduated instrument. Due to its blunt end, it can be inserted into the [[Gingiva|gingival]] sulcus without causing trauma.
| + | :[[Periodontal Probe]] |
| − | | + | :[[Dental Explorer]] |
| − | The periodontal probe is used to:
| + | :[[Dental Mirror]] |
| − | *Measure periodontal probing depth
| + | |image = Oral examination instruments.jpg |
| − | *Determine degree of gingival inflammation by gentle probing
| + | |resources = |
| − | *Measure gingival attachment loss (recession)
| + | }} |
| − | *Evaluate furcation lesions
| |
| − | *Evaluate extent of tooth mobility
| |
| − | | |
| − | The markings are either engraved rings or colour coded bands. A screening probe for example has 3 or 4mm banded block markings whilst a Williams periodontal probe is more accurate with mm markings. Before using the probe, the operator should ensure that they know what the marking represent by comparing it do a ruler.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:Modified pen grip.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Correct way to hold a periodontal probe, modified pen grip.<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]] | |
| − | [[File:Periodontal probe 3.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Periodontal probe (14W type) showing graduations of the tip<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]] | |
| − | [[File:Periodontal probe in situ.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Periodontal probe used to measure gingival sulcus depth and feel for attachment loss. Here the probing depth is 2mm and considered normal on a canine tooth<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]]
| |
| − | ===Dental Explorer=== | |
| − | | |
| − | The dental explorer or probe, a sharp-ended instrument.
| |
| − | | |
| − | It is used to check for hard tissue defects for example:
| |
| − | *Determine the presence of caries
| |
| − | *Explore other enamel and dentin defects, such as fractured teeth, odontoclastic resorptive lesions
| |
| − | | |
| − | The explorer is also useful for tactile examination of the subgingival tooth surfaces. Subgingival calculus and odontoclastic resorptive lesions may be identified in this way.
| |
| − | Dental explorers are available in various shapes, usually straight or curved. The Shepherds hook pattern is frequently used in veterinary dentistry, but a probe with a 90 degree bend is often easier to use, and more ideal.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Dental Mirror=== | |
| − | [[File:Dental_mirror.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Dental mirror<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]]
| |
| − | A dental mirror not often used in veterinary dentistry but is a useful tool as it allows you to visualise the palatal/lingual surfaces of the teeth easily. Orientation may cause confusion and the use of a dental mirror takes some practice. The mirror can be wiped across the buccal mucous membranes before use to prevent condensation occurring.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Dental mirrors are available in several sizes. A small (paediatric size) mirror for cats and small dogs and a larger one for medium to large dogs should be available.
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | + | {{Waltham}} |
| | | | |
| | + | {{OpenPages}} |
| | | | |
| | [[Category:Oral Examination]] | | [[Category:Oral Examination]] |
| | [[Category:Dental Instruments]] | | [[Category:Dental Instruments]] |
| − | [[Category:To Do - Dentistry Images]] | + | [[Category:Oral Examination Instruments - Small Animal]] |
| | + | [[Category:Waltham reviewed]] |