Difference between revisions of "Category:Rhabdoviridae"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with '{{unfinished}} =Introduction= Rabies is a neurological killer that has evolved a fool-proof technique of transmission, and it cleverly evades the species barrier to present …') |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{frontpage |
| − | + | |pagetitle =Rhabdoviridae | |
| − | = | + | |pagebody =<div style="text-align: left; direction: ltr; margin-left: 1em;"> |
[[Rabies]] is a neurological killer that has evolved a fool-proof technique of transmission, and it cleverly evades the species barrier to present a potent threat to mammalian life. While the simplicity of the virus ensures its transmission, it also contributes to its weakness: its monoclonal antigenicity means that a single vaccination covers all strains of the disease. Though rabies is considered endemic in parts of the developed and undeveloped world, vaccination schemes have rendered the disease controllable to a satisfactory degree. Nonetheless, infection is still largely fatal and the disease should not be taken lightly. | [[Rabies]] is a neurological killer that has evolved a fool-proof technique of transmission, and it cleverly evades the species barrier to present a potent threat to mammalian life. While the simplicity of the virus ensures its transmission, it also contributes to its weakness: its monoclonal antigenicity means that a single vaccination covers all strains of the disease. Though rabies is considered endemic in parts of the developed and undeveloped world, vaccination schemes have rendered the disease controllable to a satisfactory degree. Nonetheless, infection is still largely fatal and the disease should not be taken lightly. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |contenttitle =Content | ||
| + | |contentbody =<big><b> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <categorytree mode=pages>Rhabdoviridae</categorytree> | ||
| + | |logo =Vesicular stomatitis virus logo.png | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | =Morphology= | + | ==Morphology== |
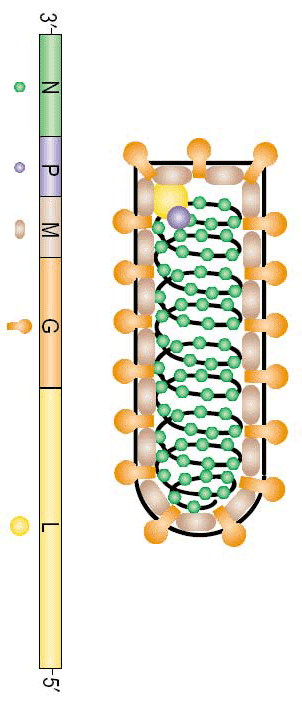
*Large, enveloped, negative-sense RNA virus | *Large, enveloped, negative-sense RNA virus | ||
*'''Bullet-shaped''' with short glycoprotein spikes | *'''Bullet-shaped''' with short glycoprotein spikes | ||
| − | =Types and Subtypes= | + | ==Types and Subtypes== |
Two Genera: | Two Genera: | ||
#Lyssaviruses: 7 genotypes | #Lyssaviruses: 7 genotypes | ||
| Line 15: | Line 22: | ||
##Genotype 4 infects '''insectivorous bats''' | ##Genotype 4 infects '''insectivorous bats''' | ||
#Vesiculoviruses are all '''exotic''' to the UK: | #Vesiculoviruses are all '''exotic''' to the UK: | ||
| − | ##Vesicular Stomatitis Virus | + | ##[[Vesicular Stomatitis Virus]] |
##Ephemeral Fever | ##Ephemeral Fever | ||
##Fish Rhabdoviruses, such as viral hemorrhagic syndrome and infectious haematopoetic necrosis virus | ##Fish Rhabdoviruses, such as viral hemorrhagic syndrome and infectious haematopoetic necrosis virus | ||
| − | = | + | |
| − | + | {{Learning |Vetstream = <P>[https://www.vetstream.com/felis/Content/Bug/bug00214.asp Rabies]</P><P>[https://www.vetstream.com/equis/Content/Disease/dis01018.asp Vesicular Stomatitis Virus]</P>}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Viruses]] | + | [[Category:Viral Organisms]] |
| + | [[Category:To_Do_-_Clinical/Viruses]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:12, 16 June 2016
Rhabdoviridae
Rabies is a neurological killer that has evolved a fool-proof technique of transmission, and it cleverly evades the species barrier to present a potent threat to mammalian life. While the simplicity of the virus ensures its transmission, it also contributes to its weakness: its monoclonal antigenicity means that a single vaccination covers all strains of the disease. Though rabies is considered endemic in parts of the developed and undeveloped world, vaccination schemes have rendered the disease controllable to a satisfactory degree. Nonetheless, infection is still largely fatal and the disease should not be taken lightly.
Morphology
- Large, enveloped, negative-sense RNA virus
- Bullet-shaped with short glycoprotein spikes
Types and Subtypes
Two Genera:
- Lyssaviruses: 7 genotypes
- Genotype 1 is classical rabies
- Genotypes 2-7 more limited in distribution
- Genotype 4 infects insectivorous bats
- Vesiculoviruses are all exotic to the UK:
- Vesicular Stomatitis Virus
- Ephemeral Fever
- Fish Rhabdoviruses, such as viral hemorrhagic syndrome and infectious haematopoetic necrosis virus
| Rhabdoviridae Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
Pages in category "Rhabdoviridae"
The following 4 pages are in this category, out of 4 total.