Difference between revisions of "Avian Liver - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <big><center>[[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO THE LIVER - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | |
| + | <big><center>[[Avian Digestive Tract - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO THE AVIAN DIGESTIVE TRACT - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| − | + | *2 lobes | |
| + | |||
| + | *Dark brown coloured (except just after hatching where it is yellow) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Right lobe larger than left lobe | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ventral and caudal to the heart (as there is no diaphragm) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *CLosely associated to the proventriculus and spleen | ||
| − | + | *Thin capsule | |
| − | |||
| + | *Indistinct lobation | ||
| + | |||
| + | *2 bile ducts enter the distal [[Duodenum - Anatomy & Physiology|duodenum]], one from each lobe of the liver | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The duct from the right lobe is connected to the [[Gall Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology|gallbladder]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Hepatic lobules indistinct (except near hilus) due to a lack of perilobular connective tissue | ||
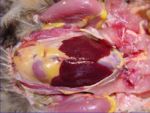
| + | [[Image:Anatomy of the Avian Liver.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Anatomy of the Liver(Avian)- Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| − | See [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology#Function|liver | + | *See [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology#Function|liver funtion]] |
==Vasculature== | ==Vasculature== | ||
| − | See [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology#Vasculature|liver vasculature]] | + | *See [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology#Vasculature|liver vasculature]] |
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
| − | See [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation|liver innervation]] | + | *See [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation|liver innervation]] |
==Lymphatics== | ==Lymphatics== | ||
| − | See [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology#Lymphatics|liver lymphatics]] | + | *See [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology#Lymphatics|liver lymphatics]] |
| + | |||
| + | ==Histology== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Polyhedral and angular cells | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Larger cells than in mammals | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Large, spherical nucleus | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Base of cell forms a wall of the sinusoid | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cell apices communicate with the bile canaliculi | ||
| − | + | *Granular cytoplasm | |
| − | + | *Liver cords form columns around the interlobular bile capillary. The cell arrangement is simpler than in mammals. | |
| − | + | *Sinusoids anastamose freely | |
| + | |||
| + | *Kupfer cells present | ||
| − | + | *Reticular fibres support the liver cords | |
| − | + | *Elastic fibres in the capsule and vessels | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Species Differences== | |
| − | + | *Pigeons and budgerigars lack a [[Gall Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology|gall bladder]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Links== | |
| − | |||
Revision as of 09:33, 15 July 2008
Structure
- 2 lobes
- Dark brown coloured (except just after hatching where it is yellow)
- Right lobe larger than left lobe
- Ventral and caudal to the heart (as there is no diaphragm)
- CLosely associated to the proventriculus and spleen
- Thin capsule
- Indistinct lobation
- 2 bile ducts enter the distal duodenum, one from each lobe of the liver
- The duct from the right lobe is connected to the gallbladder
- Hepatic lobules indistinct (except near hilus) due to a lack of perilobular connective tissue
Function
- See liver funtion
Vasculature
Innervation
Lymphatics
- See liver lymphatics
Histology
- Polyhedral and angular cells
- Larger cells than in mammals
- Large, spherical nucleus
- Base of cell forms a wall of the sinusoid
- Cell apices communicate with the bile canaliculi
- Granular cytoplasm
- Liver cords form columns around the interlobular bile capillary. The cell arrangement is simpler than in mammals.
- Sinusoids anastamose freely
- Kupfer cells present
- Reticular fibres support the liver cords
- Elastic fibres in the capsule and vessels
Species Differences
- Pigeons and budgerigars lack a gall bladder