Difference between revisions of "Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | == Introduction == |
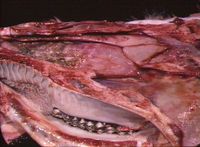
| + | [[Image:IBR nasal cavity.jpg|thumb|right|200px|<small><center>IBR in nasal cavity (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
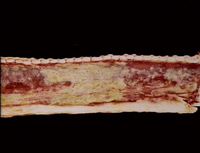
| + | [[Image:IBR trachea.jpg|thumb|right|200px|<small><center>IBR in trachea (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | This disease is also known as '''IBR''' and is caused by [[Bovine Herpesvirus 1]] (BHV-1) through aerosol transmission and close contact of infected animals. It is a highly infectious disease of cattle, causing upper respiratory tract disease. The virus is a [[:Category:Herpesviridae|herpesvirus]], meaning it has the ability to lie latent for a long period of time until reactivated by stress. | ||
| − | + | BHV-1 infects the respiratory mucosal epithelial cells (intranuclear eosinophilic inclusion bodies) from nasal mucosa down to bronchioles, which leads to neutrophilic inflammation of varying severity. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | == Classification == |
| − | |||
| − | + | BHV's Baltimore Classification is I, dsDNA virus, and is part of the Herpesviridae family. It is an enveloped virus with icosahedral capsid symmetry. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Clinical Signs == | |
| − | |||
| + | Depending on severity, one will see serous, catarrhal or purulent nasal discharge, sneezing, coughing, dyspnoea and anorexia. There will be a rhinotracheitis that can develop into [[bronchopneumonia]]. An increased respiratory rate will also be present. Pregnant cows will also be seen to abort at 5 months or later in gestation. | ||
| − | + | Clinical disease is most severe in young calves, which can develop mucosal ulcerative lesions in the oesophagus and forestomachs and viraemia with multiorgan infection. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Cattle]] | + | There is generally a high morbidity with low mortality, but up to 75% mortality if concurrent with [[Bovine Virus Diarrhoea Virus|BVDV]] resulting in meningo-encephalitis. |
| + | |||
| + | Signs can be made more severe by secondary bacterial infection such as [[:Category:Pasteurella and Mannheimia species|Pasteurella]] or [[:Category:Mycoplasmas|Mycoplasma]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Diagnosis == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Clinical signs are suggestive. Definitive diagnosis can be achieved by virus isolation and [[immunofluorescence]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | On microscopic examination of infected tissue, one will see intranuclear inclusion bodies, which are indicative of the virus. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Test for serum antibodies against IBR and re-test in 2-3 weeks time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Control == | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Vaccines|Vaccination]] '''is available and commonly used in the UK. Both vaccines available in the UK are given intranasally and neither protects against re-infection when given during clinical outbreak, but can lessen the severity of the disease. There are also '''inactivated''' vaccines: intranasal/intramuscular administration, which have a gE deletion making this a '''marker vaccine'''. There is an ELISA for gE deletion, which can enable culling of carrier animals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <big><b>For more information see [[Bovine Herpesvirus 1]]. </b></big> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Cattle Medicine Q&A 05]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Andrews, A.H, Blowey, R.W, Boyd, H and Eddy, R.G. (2004) '''Bovine Medicine '''(Second edition), ''Blackwell Publishing'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Divers, T.J. and Peek, S.F. (2008)''' Rebhun's diseases of dairy cattle,''''' Elsevier Health Scieneces'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Radostits, O.M, Arundel, J.H, and Gay, C.C. (2000) '''Veterinary Medicine: a textbook of the diseases of cattle, sheep, pigs, goats and horses, '''''Elsevier Health Sciences'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Webinars== | ||
| + | <rss max="10" highlight="none">https://www.thewebinarvet.com/respiratory/webinars/feed</rss> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Respiratory_Diseases_-_Cattle]] [[Category:Expert_Review - Farm Animal]] [[Category:Respiratory_Viral_Infections]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:02, 4 January 2023
Introduction
This disease is also known as IBR and is caused by Bovine Herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) through aerosol transmission and close contact of infected animals. It is a highly infectious disease of cattle, causing upper respiratory tract disease. The virus is a herpesvirus, meaning it has the ability to lie latent for a long period of time until reactivated by stress.
BHV-1 infects the respiratory mucosal epithelial cells (intranuclear eosinophilic inclusion bodies) from nasal mucosa down to bronchioles, which leads to neutrophilic inflammation of varying severity.
Classification
BHV's Baltimore Classification is I, dsDNA virus, and is part of the Herpesviridae family. It is an enveloped virus with icosahedral capsid symmetry.
Clinical Signs
Depending on severity, one will see serous, catarrhal or purulent nasal discharge, sneezing, coughing, dyspnoea and anorexia. There will be a rhinotracheitis that can develop into bronchopneumonia. An increased respiratory rate will also be present. Pregnant cows will also be seen to abort at 5 months or later in gestation.
Clinical disease is most severe in young calves, which can develop mucosal ulcerative lesions in the oesophagus and forestomachs and viraemia with multiorgan infection.
There is generally a high morbidity with low mortality, but up to 75% mortality if concurrent with BVDV resulting in meningo-encephalitis.
Signs can be made more severe by secondary bacterial infection such as Pasteurella or Mycoplasma.
Diagnosis
Clinical signs are suggestive. Definitive diagnosis can be achieved by virus isolation and immunofluorescence.
On microscopic examination of infected tissue, one will see intranuclear inclusion bodies, which are indicative of the virus.
Test for serum antibodies against IBR and re-test in 2-3 weeks time.
Control
Vaccination is available and commonly used in the UK. Both vaccines available in the UK are given intranasally and neither protects against re-infection when given during clinical outbreak, but can lessen the severity of the disease. There are also inactivated vaccines: intranasal/intramuscular administration, which have a gE deletion making this a marker vaccine. There is an ELISA for gE deletion, which can enable culling of carrier animals.
For more information see Bovine Herpesvirus 1.
| Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Cattle Medicine Q&A 05 |
References
Andrews, A.H, Blowey, R.W, Boyd, H and Eddy, R.G. (2004) Bovine Medicine (Second edition), Blackwell Publishing
Divers, T.J. and Peek, S.F. (2008) Rebhun's diseases of dairy cattle, Elsevier Health Scieneces
Radostits, O.M, Arundel, J.H, and Gay, C.C. (2000) Veterinary Medicine: a textbook of the diseases of cattle, sheep, pigs, goats and horses, Elsevier Health Sciences
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/respiratory/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS