Difference between revisions of "Soft Palate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
(→Canine) |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <big><center>[[Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO ALIMENTARY - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | The soft palate (velum palatine) is located caudally to the [[Hard Palate|hard palate]] | + | The soft palate (velum palatine) is located caudally to the [[Hard Palate - Anatomy & Physiology|hard palate]]. It is comprised of muscle and is involved in tasting food and in [[deglutition]]. |
| + | |||
| − | |||
==Structure and Function== | ==Structure and Function== | ||
| − | + | *Muscle | |
| + | |||
| + | *Contacts [[Epiglottis|epiglottis]] caudally | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Very folded mucosa | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Striated palatine muscle | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Histology== | ||
| + | |||
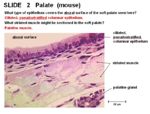
| + | [[Image:Soft Palate Mouse.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Soft Palate (Mouse) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| + | *Respiratory mucosa - ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium on aboral surface | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Stratified squamous epithelium on oral surface | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Palatine|Palatine]] salivary glands | ||
| − | |||
==Musculature and Innervation== | ==Musculature and Innervation== | ||
| − | + | *Sensation and taste from glossopharyngeal ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN IX]]) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Palatine muscle | |
| − | + | **Origin: hard palate transeverse ridges | |
| − | [[ | + | **Insertion: soft palate |
| + | **Shortens palate | ||
| + | **Major innervation from vagus nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN X]]) **Minor from glossopgaryngeal nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN IX]]) | ||
| − | + | *Tensor velli palatini | |
| − | + | **Origin: near tympanic bulla on temporal bone | |
| + | **Insertion: lateral aponeurosis | ||
| + | **Pharyngeal arch 1 | ||
| + | **Mandibular of trigeminal ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN V3]]) | ||
| + | **Tenses soft palate | ||
| − | + | *Levator velli palatini | |
| − | + | **Origin: near tympanic bulla on temporal bone | |
| + | **Insertion: lateral aponeurosis | ||
| + | **Raises soft palate | ||
| + | **Major innervation from vagus nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN X]]) and minor from glossopgaryngeal nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN IX]]) | ||
| − | + | *Palatopharyngeus | |
| − | [[ | + | **closes palatopharyngeal arch and therefore lift soft palate |
| − | + | **Major innervation from vagus nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN X]]) | |
| + | **Minor from glossopgaryngeal nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN IX]]) | ||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
===Porcine=== | ===Porcine=== | ||
| − | + | *Soft palate does not contact the [[Epiglottis|epiglottis]] as the porcine soft palate is raised higher in the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|oral cavity ]] than in other species | |
===Equine=== | ===Equine=== | ||
| − | + | *Tight laryngeal cuff around the laryngeal entrance therefore the soft palate cannot be raised for long periods of time and thus horses are nasal breathers | |
===Canine=== | ===Canine=== | ||
| − | As brachiocephalic breeds have a shortened skull length, the soft palate | + | *As brachiocephalic breeds have a shortened skull length, the soft palate often obstruct air flow into the [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology|larynx]] causing breathing difficulties |
===Avian=== | ===Avian=== | ||
| − | Birds lack a soft palate | + | *Birds lack a soft palate |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | <big><center>[[Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO ALIMENTARY - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> |
Revision as of 10:36, 23 July 2008
Introduction
The soft palate (velum palatine) is located caudally to the hard palate. It is comprised of muscle and is involved in tasting food and in deglutition.
Structure and Function
- Muscle
- Contacts epiglottis caudally
- Very folded mucosa
- Striated palatine muscle
Histology
- Respiratory mucosa - ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium on aboral surface
- Stratified squamous epithelium on oral surface
- Palatine salivary glands
Musculature and Innervation
- Sensation and taste from glossopharyngeal (CN IX)
- Palatine muscle
- Tensor velli palatini
- Origin: near tympanic bulla on temporal bone
- Insertion: lateral aponeurosis
- Pharyngeal arch 1
- Mandibular of trigeminal (CN V3)
- Tenses soft palate
- Levator velli palatini
- Palatopharyngeus
Species Differences
Porcine
- Soft palate does not contact the epiglottis as the porcine soft palate is raised higher in the oral cavity than in other species
Equine
- Tight laryngeal cuff around the laryngeal entrance therefore the soft palate cannot be raised for long periods of time and thus horses are nasal breathers
Canine
- As brachiocephalic breeds have a shortened skull length, the soft palate often obstruct air flow into the larynx causing breathing difficulties
Avian
- Birds lack a soft palate