Difference between revisions of "Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (30 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <big><center>[[Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO ALIMENTARY - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | |
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | The [[Pharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|pharynx]] is the chamber connecting the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|oral cavity]], [[Nasal | + | The [[Pharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|pharynx]] is the chamber connecting the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|oral cavity]], [[Nasal cavity - Anatomy & Physiology|nasal cavity]], [[Oesophagus - Anatomy & Physiology|oesophagus]] and [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology|larynx]]. The [[Pharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|pharynx]] is divided into the [[Nasopharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|nasopharynx]], oropharynx and [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology#Laryngeal Pharynx|laryngeal pharynx]] which all have different functions, innervation and develope differently. |
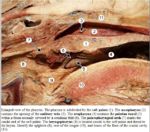
| − | [[Image:Pharynx Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right| | + | |
| + | The oropharynx is the oral section of the [[Pharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|pharynx]]. | ||
| + | [[Image:Pharynx Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Pharynx Labelled - Copyright C.Clarkson and T.F.Fletcher University of Minnesota]] | ||
==Structure and Function== | ==Structure and Function== | ||
| − | + | *Last molar rostrally | |
| + | |||
| + | *[[Epiglottis]] caudally | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Oral Cavity - Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|Tongue]] ventrally | ||
| − | + | *[[Soft Palate - Anatomy & Physiology|Soft palate]] dorsally | |
| − | + | *Endoderm | |
| + | |||
| + | *Innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN IX]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Divided by glossopalatine arch from [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology#Laryngeal Pharynx|laryngeal pharynx]] | ||
| − | |||
==Musculature== | ==Musculature== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 29: | ||
'''Constrictors''' | '''Constrictors''' | ||
| − | + | *Hyopharyngeus | |
| + | |||
| + | *Thyropharyngeus | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cricopharyngeus | ||
'''Dilators''' | '''Dilators''' | ||
| − | + | *Stylopharyngeus | |
| + | |||
| + | '''Shorten''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Pterygopharyngeus | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Close Pharyngeal Arch''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Palatopharyngeus | ||
| − | |||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
| − | Muscles from | + | *Muscles from pharyngeal arch 4 innervated by vagus nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN X]]) |
| + | |||
| + | *Stylopharyngeus from pharyngeal arch 3 innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN IX]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Histology== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Stratified squamous epithelium | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Keratinised in ruminants | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Lamina propria contains aggregates of lymphoid tissue (called tonsils) in several parts of the oropharynx | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Links== | ||
| − | + | [[Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards#Oropharynx Flashcards|Oropharynx Flashcards]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | <big><center>[[Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO ALIMENTARY - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | |
| − | [[ | ||
Revision as of 12:27, 31 July 2008
Introduction
The pharynx is the chamber connecting the oral cavity, nasal cavity, oesophagus and larynx. The pharynx is divided into the nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngeal pharynx which all have different functions, innervation and develope differently.
The oropharynx is the oral section of the pharynx.
Structure and Function
- Last molar rostrally
- Epiglottis caudally
- Tongue ventrally
- Soft palate dorsally
- Endoderm
- Innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- Divided by glossopalatine arch from laryngeal pharynx
Musculature
Constrictors
- Hyopharyngeus
- Thyropharyngeus
- Cricopharyngeus
Dilators
- Stylopharyngeus
Shorten
- Pterygopharyngeus
Close Pharyngeal Arch
- Palatopharyngeus
Innervation
- Muscles from pharyngeal arch 4 innervated by vagus nerve (CN X)
- Stylopharyngeus from pharyngeal arch 3 innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Histology
- Stratified squamous epithelium
- Keratinised in ruminants
- Lamina propria contains aggregates of lymphoid tissue (called tonsils) in several parts of the oropharynx