Difference between revisions of "Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
|||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{toplink |
| − | [[Image:Rumen Topography Sheep.jpg|thumb|right| | + | |backcolour =BCED91 |
| + | |linkpage =Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |linktext =Alimentary System | ||
| + | |maplink = Alimentary (Concept Map)- Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |pagetype =Anatomy | ||
| + | |subtext1=STOMACH AND ABOMASUM | ||
| + | |sublik1=Stomach and Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
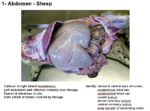
| + | [[Image:Rumen Topography Sheep.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Rumen Topography (Sheep) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | + | The rumen is the first chamber of the ruminant stomach. It is the largest chamber and has regular contractions to move food around for digestion, eliminate gases through [[Eructation - Anatomy & Physiology|eructation]] and send food particles back to the mouth for [[Mastication|remastication]]. | |
| − | + | The rumen breaks down food particles through mechanical digestion and fermentation with the help of symbiotic microbes. [[Volatile Fatty Acids - Anatomy & Physioogy|Volatile fatty acids]] are the main product of ruminant digestion. | |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| − | [[Image:Rumen Anatomy Sheep.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Rumen Anatomy Sheep.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Rumen Anatomy (Sheep) - Copyright RVC 2008]] |
| − | Grooves correspond with thickened smooth muscle pillars on the inside of the rumen | + | *Grooves correspond with thickened smooth muscle pillars on the inside of the rumen |
| + | **Ruminal pillars divide the dorsal and ventral ruminal sacs | ||
| + | **Coronary pillars divide the caudal blind sacs | ||
| + | **Cranial pillar divides the dorsal and cranial sacs | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Covered by greater omentum | ||
| + | |||
| + | *38-40°C | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Anaerobic | ||
| + | |||
| + | *pH 6.7 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Buffered | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Large holding capacity | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Water intake lowers the ruminal temperature so bacteria are tolerant to temperature changes towards the lower end of the scale | ||
| − | The | + | *Objects are often lodged in the rumino-reticular fold. When the rumen contracts, the object can be pushed through the [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]] wall into the [[Structure of the Heart - Anatomy & Physiology#Pericardium|pericardium]] and [[Heart - Anatomy & Physiology|heart]]. |
| + | |||
| + | *Laterally compressed | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Extends from the cardia at the level of the 8th rib to the pelvic inlet | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Serosa covers the entire rumen except dorsally where the rumen attaches to the abdominal roof allowing more freedom for ruminal movement and expansion | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ruminal contractions can be felt for in the left paralumbar fossa | ||
| + | |||
| + | *1-2 contractions should be felt per minute | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Opening at the cardia into both the rumen and [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]] is called the reticuluar groove (see [[Oesophageal groove|oesophageal groove]]) | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| − | + | *Waste removal | |
| + | |||
| + | *Simpler products of digestion are assilimated directly, others continue down the digestive tract for further digestion | ||
| − | See [[Rumination|rumination]] | + | *Mixes food |
| + | |||
| + | *Moves food forwards through the stomach chambers | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Sensors in the rumen can determine the courseness of the food. Course, tough feed needs stronger and more frequent ruminal contractions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Vagus nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN X]]) is needed for control of stomach movements | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reflex control through sensory receptors in the medulla | ||
| + | |||
| + | *See [[Rumination - Anatomy & Physiology|rumination]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *See [[Eructation - Anatomy & Physiology|eructation]] | ||
==Ruminoreticular contraction== | ==Ruminoreticular contraction== | ||
| − | [[Image:Contractions of the ruminoreticulum diagram.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Contractions of the ruminoreticulum diagram.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Diagram of the contractions of the ruminoreticulum - Copyright RVC 2008]] |
| + | *Primary mixes food | ||
| + | **Mixing cycle of ruminoreticulum | ||
| + | **2 contractions of the [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]] (2nd most powerful) which continues over the rumen | ||
| + | **Ingesta flows from the [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]] to cranial ruminal sac to [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]] (or ventral sac) | ||
| + | **Every 60 seconds | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Secondary lets gas out | ||
| + | **See [[Eructation - Anatomy & Physiology|eructation]] | ||
| + | **Ingesta flows from ventral blind sac to dorsal blind sac to dorsal sac ([[Eructation - Anatomy & Physiology|eructation]]) to ventral sac | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Vasculature== | ||
| − | + | *Cranial mesenteric artery | |
| − | |||
| − | + | *Celiac artery | |
| − | + | *Right and left ruminal arteries | |
| − | |||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
| − | + | *Dorsal vagus ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN X]]) (most important) | |
| + | |||
| + | *Ventral vagus ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN X]]) | ||
==Lymphatics== | ==Lymphatics== | ||
| − | + | *Caudal mediastinal lymph node enlargement put pressure on the dorsal vagus effecting ruminal contractions | |
| + | |||
| + | *Numerous small lymph nodes are scattered in the ruminal grooves | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The lymph drains to larger atrial nodes between the cardia and [[The Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology|omasum]], then to the cistera chyli | ||
| + | |||
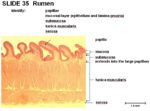
| + | ==Histology== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Rumen Histology Sheep.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Rumen Histology (Sheep) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| + | *Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Non-glandular | ||
| + | |||
| + | *No lamina muscularis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *2 thick layers of tunica muscularis- inner circular and outer longitudinal | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Interior surface of the rumen forms numerous papillae | ||
| + | **Papillae can be long and foliate | ||
| + | **Papillae can be short and pointed | ||
| + | **Up to 6mm in length | ||
| + | **Animals fed on rough grass or in the dry season have longer papillae | ||
| + | **Animals fed on digestible feed or in the wet season have shorter papillae (1-2mm in length) | ||
| + | **Fewer dorsally | ||
| + | **Increase surface area for [[Volatile Fatty Acids - Anatomy & Physioogy|volatile fatty acid]] absorption | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The upper keratinised layer of papillae protects against abrasion | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The deeper layers of papillae metabolise the [[Volatile Fatty Acids - Anatomy & Physioogy|volatile fatty acids]] | ||
==Rumen Microbes== | ==Rumen Microbes== | ||
| − | + | *Have a variety of microbes that can utilise many substrates | |
| + | |||
| + | *Dominance of different bacterial species depends on pH. Ergo, microbial populations are not constant | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Microbes digest cellulose and hemi-cellulose | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Microbes provide a source of all amino acids | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Microbes synthesise vitamins (especially the B vitamins) | ||
| − | + | '''Rumen Microbial Population''' | |
| − | + | *Bacteria | |
| − | + | **Over 2000 species | |
| + | **99.5% obligate anaerobes | ||
| − | + | *Protozoa | |
| − | Large | + | **Large |
| + | **Unicellular organisms | ||
| + | **Prey on bacteria | ||
| + | **Numbers affected by diet | ||
| − | + | *Fungi | |
| − | Digest fibre | + | **Digest fibre |
| + | **Numbers present usually low | ||
'''Common Rumen Microbes''' | '''Common Rumen Microbes''' | ||
| Line 62: | Line 167: | ||
!'''pH''' | !'''pH''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | '''Ruminococcus flavefauens''' |
| Fibre | | Fibre | ||
| 6.15 | | 6.15 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | '''Fibrobacter succinogens''' |
| Fibre | | Fibre | ||
| 6 | | 6 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | '''Megashpaera eisdeni''' |
| Lactate user | | Lactate user | ||
| 4.9 | | 4.9 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | '''Streptococcus bovis''' |
| Lactate producer | | Lactate producer | ||
| 4.55 | | 4.55 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Species Differences== |
| − | + | ===Small Ruminats=== | |
| − | + | *Sheep and goats have a larger ventral ruminal sac than dorsal ruminal sac | |
| − | + | *Cranial mesenteric artery and celiac artery come off the same root | |
| − | == | + | ===Bovine=== |
| + | *Cranial mesenteric artery and celiac artery are close in the cow | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Dairy cows have a rumen pH of 5.5 due to more digestible feed | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Links== | ||
| − | + | [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology]] | |
| − | + | [[The Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology|The Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology]] | |
| − | + | [[The Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology|The Abomasum- Anatomy & Physiology]] | |
| − | The | + | [[The Stomachs of the Ruminant - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards#The Rumen|The Rumen Flashcards]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Video''' | |
| − | + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/bovine/Pot0052.mp4 Pot 52 Lateral view of the Abdomen of a young Ruminant] | |
| − | + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/bovine/pot0175.mp4 Pot 175 Sections of the Ruminant Stomach] | |
| − | + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Frean/sheep/LeftSideTopography.mp4 Left sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen and Thorax] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Frean/sheep/RightSideTopography.mp4 Right sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen] | |
| − | |||
| − | [ | + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Frean/sheep/RuminantStomachStructure.mp4 Structure of the ruminant forestomachs] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 23:28, 25 August 2008
|
|
Introduction
The rumen is the first chamber of the ruminant stomach. It is the largest chamber and has regular contractions to move food around for digestion, eliminate gases through eructation and send food particles back to the mouth for remastication.
The rumen breaks down food particles through mechanical digestion and fermentation with the help of symbiotic microbes. Volatile fatty acids are the main product of ruminant digestion.
Structure
- Grooves correspond with thickened smooth muscle pillars on the inside of the rumen
- Ruminal pillars divide the dorsal and ventral ruminal sacs
- Coronary pillars divide the caudal blind sacs
- Cranial pillar divides the dorsal and cranial sacs
- Covered by greater omentum
- 38-40°C
- Anaerobic
- pH 6.7
- Buffered
- Large holding capacity
- Water intake lowers the ruminal temperature so bacteria are tolerant to temperature changes towards the lower end of the scale
- Objects are often lodged in the rumino-reticular fold. When the rumen contracts, the object can be pushed through the reticulum wall into the pericardium and heart.
- Laterally compressed
- Extends from the cardia at the level of the 8th rib to the pelvic inlet
- Serosa covers the entire rumen except dorsally where the rumen attaches to the abdominal roof allowing more freedom for ruminal movement and expansion
- Ruminal contractions can be felt for in the left paralumbar fossa
- 1-2 contractions should be felt per minute
- Opening at the cardia into both the rumen and reticulum is called the reticuluar groove (see oesophageal groove)
Function
- Waste removal
- Simpler products of digestion are assilimated directly, others continue down the digestive tract for further digestion
- Mixes food
- Moves food forwards through the stomach chambers
- Sensors in the rumen can determine the courseness of the food. Course, tough feed needs stronger and more frequent ruminal contractions.
- Vagus nerve (CN X) is needed for control of stomach movements
- Reflex control through sensory receptors in the medulla
- See rumination
- See eructation
Ruminoreticular contraction
- Primary mixes food
- Secondary lets gas out
- See eructation
- Ingesta flows from ventral blind sac to dorsal blind sac to dorsal sac (eructation) to ventral sac
Vasculature
- Cranial mesenteric artery
- Celiac artery
- Right and left ruminal arteries
Innervation
- Dorsal vagus (CN X) (most important)
- Ventral vagus (CN X)
Lymphatics
- Caudal mediastinal lymph node enlargement put pressure on the dorsal vagus effecting ruminal contractions
- Numerous small lymph nodes are scattered in the ruminal grooves
- The lymph drains to larger atrial nodes between the cardia and omasum, then to the cistera chyli
Histology
- Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
- Non-glandular
- No lamina muscularis
- 2 thick layers of tunica muscularis- inner circular and outer longitudinal
- Interior surface of the rumen forms numerous papillae
- Papillae can be long and foliate
- Papillae can be short and pointed
- Up to 6mm in length
- Animals fed on rough grass or in the dry season have longer papillae
- Animals fed on digestible feed or in the wet season have shorter papillae (1-2mm in length)
- Fewer dorsally
- Increase surface area for volatile fatty acid absorption
- The upper keratinised layer of papillae protects against abrasion
- The deeper layers of papillae metabolise the volatile fatty acids
Rumen Microbes
- Have a variety of microbes that can utilise many substrates
- Dominance of different bacterial species depends on pH. Ergo, microbial populations are not constant
- Microbes digest cellulose and hemi-cellulose
- Microbes provide a source of all amino acids
- Microbes synthesise vitamins (especially the B vitamins)
Rumen Microbial Population
- Bacteria
- Over 2000 species
- 99.5% obligate anaerobes
- Protozoa
- Large
- Unicellular organisms
- Prey on bacteria
- Numbers affected by diet
- Fungi
- Digest fibre
- Numbers present usually low
Common Rumen Microbes
| Species | Type | pH |
|---|---|---|
| Ruminococcus flavefauens | Fibre | 6.15 |
| Fibrobacter succinogens | Fibre | 6 |
| Megashpaera eisdeni | Lactate user | 4.9 |
| Streptococcus bovis | Lactate producer | 4.55 |
Species Differences
Small Ruminats
- Sheep and goats have a larger ventral ruminal sac than dorsal ruminal sac
- Cranial mesenteric artery and celiac artery come off the same root
Bovine
- Cranial mesenteric artery and celiac artery are close in the cow
- Dairy cows have a rumen pH of 5.5 due to more digestible feed
Links
The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology
The Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology
The Abomasum- Anatomy & Physiology
Video
Pot 52 Lateral view of the Abdomen of a young Ruminant
Pot 175 Sections of the Ruminant Stomach
Left sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen and Thorax