Difference between revisions of "Yeast-like Fungi - Flashcards"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (17 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |backcolour = f5fffa | ||
| + | |linkpage =Yeast-like fungi | ||
| + | |linktext =YEAST-LIKE FUNGI | ||
| + | |sublink1 =Flash Cards - WikiBugs | ||
| + | |subtext1 =WIKIBUGS FLASHCARDS | ||
| + | |pagetype =Bugs | ||
| + | }} | ||
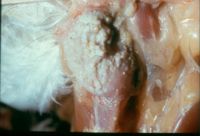
[[Image:Sour Crop.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Sour Crop - Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath]] | [[Image:Sour Crop.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Sour Crop - Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath]] | ||
| − | ===Candidosis=== | + | ==<font color="purple">Candidosis</font>== |
| − | + | {| border="3" cellpadding="8" | |
| − | | | + | !width="400"|'''Question''' |
| − | | | + | !width="400"|'''Answer''' |
| − | *C. albicans | + | !width="150"|'''Article''' |
| − | *C. tropicalis | + | |- |
| − | *C. pelliculosa | + | |<big>'''What are the three important species of ''Candida'' in animal infections?''' |
| − | | | + | ||<font color="white"> <big> |
| − | | | + | *'''''C. albicans''''' |
| − | | | + | *'''''C. tropicalis''''' |
| − | *White-grey lesions in mouth, oesophagus and crop | + | *'''''C. pelliculosa''''' |
| − | *Thickened crop wall | + | ||[[Yeast-like fungi#Candidosis|<span title="Answer article">Link to Answer Article</span>]] |
| − | *Yellow-white necrotic material in crop | + | |- |
| − | | | + | |<big>'''What are the clinical signs of a sour crop infection?''' |
| − | | | + | ||<font color="white"> <big> |
| − | | | + | *'''''White-grey lesions in mouth, oesophagus and crop''''' |
| − | *Thrush in humans | + | *'''''Thickened crop wall''''' |
| − | *Metritis, pyometra and vaginitis in mares | + | *'''''Yellow-white necrotic material in crop''''' |
| − | *Genital candidiosis in stallions | + | ||[[Yeast-like fungi#Candidosis|<span title="Answer article">Link to Answer Article</span>]] |
| − | *Bovine mastitis | + | |- |
| − | *Porcine stomach ulcers | + | |<big>'''What other conditions are ''Candida'' spp. implicated in?''' |
| − | | | + | ||<font color="white"> <big> |
| − | | | + | *'''''Thrush in humans''''' |
| − | | | + | *'''''Metritis, pyometra and vaginitis in mares''''' |
| − | *Skin scrapings in 20% KOH for microscopy | + | *'''''Genital candidiosis in stallions''''' |
| − | *Lactophenol Cotton Blue and stained by Gram or Methylene Blue stain | + | *'''''Bovine mastitis''''' |
| − | *Grows on Blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar | + | *'''''Porcine stomach ulcers''''' |
| − | *Gram positive, oval, thin-walled budding cells with hyphal fragments | + | ||[[Yeast-like fungi#Candidosis|<span title="Answer article">Link to Answer Article</span>]] |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |<big>'''How would you demonstrate a ''Candida'' infection?''' | |
| − | + | ||<font color="white"> <big> | |
| − | + | *'''''Skin scrapings in 20% KOH for microscopy''''' | |
| − | + | *'''''Lactophenol Cotton Blue and stained by Gram or Methylene Blue stain''''' | |
| − | + | *'''''Grows on Blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar''''' | |
| − | + | *'''''Gram positive, oval, thin-walled budding cells with hyphal fragments''''' | |
| − | + | ||[[Yeast-like fungi#Candidosis|<span title="Answer article">Link to Answer Article</span>]] | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | | | + | <br> |
| − | + | ==<font color="purple">Cryptococcosis</font>== | |
| − | + | {| border="3" cellpadding="8" | |
| − | + | !width="400"|'''Question''' | |
| − | + | !width="400"|'''Answer''' | |
| − | | | + | !width="150"|'''Article''' |
| − | | | + | |- |
| − | | | + | |<big>'''What are the three important species of ''Candida'' in animal infections?''' |
| − | + | ||<font color="white"> <big> | |
| − | + | *'''''C. albicans''''' | |
| − | + | *'''''C. tropicalis''''' | |
| − | + | *'''''C. pelliculosa''''' | |
| − | + | ||[[Yeast-like fungi#Cryptococcosis|<span title="Answer article">Link to Answer Article</span>]] | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
| − | |||
| − | === | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
Revision as of 12:26, 17 May 2009
|
|
Candidosis
| Question | Answer | Article |
|---|---|---|
| What are the three important species of Candida in animal infections? |
|
Link to Answer Article |
| What are the clinical signs of a sour crop infection? |
|
Link to Answer Article |
| What other conditions are Candida spp. implicated in? |
|
Link to Answer Article |
| How would you demonstrate a Candida infection? |
|
Link to Answer Article |
Cryptococcosis
| Question | Answer | Article |
|---|---|---|
| What are the three important species of Candida in animal infections? |
|
Link to Answer Article |