Difference between revisions of "Toxoplasma gondii"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (20 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
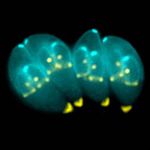
| − | + | [[Image:Toxoplasma gondii.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma gondii'' - Ke Hu and John Murray]] | |
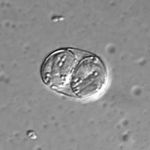
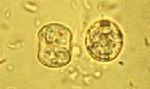
| − | [[Image:Toxoplasma gondii.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma gondii'' | + | [[Image:Toxoplasma sporulated oocyst.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma'' Sporulated Oocyst - Wikimedia Commons]] |
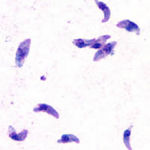
| + | [[Image:Toxoplasma Tacchyzoites.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma'' Tacchyzoites - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
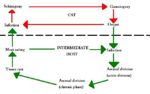
[[Image:Toxoplasma Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | [[Image:Toxoplasma Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | ||
[[Image:Toxoplasma gondii 2.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma gondii'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | [[Image:Toxoplasma gondii 2.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma gondii'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | ||
| − | + | *Major pathogenic species called ''Toxoplasma gondii'' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Causes disease in a wide range of animal species including humans | |
| − | + | *Important cause of abortion in sheep | |
| − | + | *Zoonotic | |
| + | **Can cause abortion | ||
| + | **Can cause congenitally aquired defects | ||
| − | + | *Forms a sporulated oocyst which is only 10μm | |
| + | **Contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites | ||
| − | + | *Transmission through ingesting the intermediate host or via the faecal-oral route | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Life Cycle''' | |
| − | + | *Complex | |
| − | + | *Usually indirect | |
| + | **Referred to as '''facultatively heteroxenous''' | ||
| + | **Intermediate host is not essential for completion of the life cycle | ||
| − | + | *Gametogony (sexual stage) is host specific for felids | |
| − | + | *Any warm blooded animal can act as a facultative intermediate host | |
| − | + | **Asexual reproduction occurs in the intermediate host forming tissue cysts | |
| − | + | **Intermediate host swallows sporulated oocysts or tissue cysts | |
| + | **Can be transferred between intermediate hosts by carnivorism | ||
| − | + | *Cats | |
| − | + | **Sporulation occurs in 2-3 days | |
| + | **Cats either swallow infective (sporulated) oocysts where ''Toxoplasma gondii'' has a prepatent period of 3 weeks | ||
| + | **Or eat the tissues of an infected intermediate host where ''Toxoplasma gondii'' has a prepatent period of 3-10 days | ||
| + | **Self-limiting infection | ||
| + | **Oocysts are shed for 1-2 weeks | ||
| + | ***Shedding can occur later if immunity wanes or cat is immuno-compromised | ||
| − | + | *Intermediate host | |
| − | + | **3 sources of infection | |
| + | ***Oocysts from environment contaminated by cat faeces | ||
| + | ***Eating cysts in tissues of other infected hosts through carnivorism or undercooked meat | ||
| + | ***Transplacental transmission in some host species during the acute phase of infection | ||
| − | + | *Acute phase of infection | |
| + | **After infection of the intermediate host the organism undergoes a phase of rapid division and dissemination throughout the body | ||
| + | ***Parasite enters cell and asexual reproduction occurs by '''endodyogeny''' (budding) producing 8-16 '''tachyzoites''' | ||
| + | ***Tachyzoites are released when host cell bursts | ||
| + | ***Haematogenous spread as more cells are infected | ||
| + | ***Infection continues until the animal develops immunity (around 2 weeks) at which point the infection enters the chronic phase | ||
| + | *Chronic phase of infection | ||
| + | **Occurs once the host's immune response has become effective | ||
| + | ***Groups of slow growing intracellular '''bradyzoites''' become walled off forming infective '''cysts''' | ||
| + | ***Bradyzoites inside cysts are protected from the host immune response whereas extracellular tachyzoites are killed | ||
| + | ***Cysts remain viable for months to years and are particularly numerous in muscle and nervous tissue | ||
| + | ***If immunity is suppressed the infection can revert to the acute form | ||
| − | + | *Meat animals | |
| + | **Significant proportion of cattle, sheep, pigs and rabbits can tissue cysts | ||
| − | + | '''Pathogenesis''' | |
| − | + | *Cattle and horses | |
| + | **Sometimes infectious causing opthalmitis | ||
| + | *Dogs | ||
| + | **Complication of canine distemper | ||
| + | **Causes [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology#Toxoplasmosis|pneumonia]] and encephalitis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Toxoplasma can cause [[Pancreas Inflammatory - Pathology#Acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis|acute interstitial pancreatitis]] in systemic toxoplasmosis | ||
| − | '''[[ | + | *''Toxoplasma gondii'' causes [[Muscles Inflammatory - Pathology#Protozoa|myositis]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | <big>'''[[Toxoplasmosis - Cat|Cat Toxoplasmosis]] | ||
| − | + | '''[[Toxoplasmosis - Sheep|Sheep Toxoplasmosis]] | |
| − | + | '''[[Toxoplasmosis - Human|Human Toxoplasmosis]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Tissue_Cyst_Forming_Coccidia]] | [[Category:Tissue_Cyst_Forming_Coccidia]] | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 23:13, 9 April 2010
- Major pathogenic species called Toxoplasma gondii
- Causes disease in a wide range of animal species including humans
- Important cause of abortion in sheep
- Zoonotic
- Can cause abortion
- Can cause congenitally aquired defects
- Forms a sporulated oocyst which is only 10μm
- Contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites
- Transmission through ingesting the intermediate host or via the faecal-oral route
Life Cycle
- Complex
- Usually indirect
- Referred to as facultatively heteroxenous
- Intermediate host is not essential for completion of the life cycle
- Gametogony (sexual stage) is host specific for felids
- Any warm blooded animal can act as a facultative intermediate host
- Asexual reproduction occurs in the intermediate host forming tissue cysts
- Intermediate host swallows sporulated oocysts or tissue cysts
- Can be transferred between intermediate hosts by carnivorism
- Cats
- Sporulation occurs in 2-3 days
- Cats either swallow infective (sporulated) oocysts where Toxoplasma gondii has a prepatent period of 3 weeks
- Or eat the tissues of an infected intermediate host where Toxoplasma gondii has a prepatent period of 3-10 days
- Self-limiting infection
- Oocysts are shed for 1-2 weeks
- Shedding can occur later if immunity wanes or cat is immuno-compromised
- Intermediate host
- 3 sources of infection
- Oocysts from environment contaminated by cat faeces
- Eating cysts in tissues of other infected hosts through carnivorism or undercooked meat
- Transplacental transmission in some host species during the acute phase of infection
- 3 sources of infection
- Acute phase of infection
- After infection of the intermediate host the organism undergoes a phase of rapid division and dissemination throughout the body
- Parasite enters cell and asexual reproduction occurs by endodyogeny (budding) producing 8-16 tachyzoites
- Tachyzoites are released when host cell bursts
- Haematogenous spread as more cells are infected
- Infection continues until the animal develops immunity (around 2 weeks) at which point the infection enters the chronic phase
- After infection of the intermediate host the organism undergoes a phase of rapid division and dissemination throughout the body
- Chronic phase of infection
- Occurs once the host's immune response has become effective
- Groups of slow growing intracellular bradyzoites become walled off forming infective cysts
- Bradyzoites inside cysts are protected from the host immune response whereas extracellular tachyzoites are killed
- Cysts remain viable for months to years and are particularly numerous in muscle and nervous tissue
- If immunity is suppressed the infection can revert to the acute form
- Occurs once the host's immune response has become effective
- Meat animals
- Significant proportion of cattle, sheep, pigs and rabbits can tissue cysts
Pathogenesis
- Cattle and horses
- Sometimes infectious causing opthalmitis
- Dogs
- Complication of canine distemper
- Causes pneumonia and encephalitis
- Toxoplasma can cause acute interstitial pancreatitis in systemic toxoplasmosis
- Toxoplasma gondii causes myositis