Difference between revisions of "Subcutaneous Mycoses"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Category:Subcutaneous Mycoses) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | # | + | {{unfinished}} |
| + | |||
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |backcolour = | ||
| + | |linkpage =Fungi | ||
| + | |linktext =FUNGI | ||
| + | |pagetype=Bugs | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Chromoblastomycosis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Chromomycosis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Epizootic Lymphangitis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Eumycotic Mycetoma]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Hyphomycosis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Pythiosis== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Causes Mycotic Swamp Fever | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Also called phycomycosis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Occurs in the USA, Australia, New Guinea, India, Brazil, Colombia, Japan, Costa Rica and Indonesia | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Pythium insidiosum'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Enters via wounds | ||
| + | **[[Lips - Anatomy & Physiology|Lips]], [[Musculoskeletal System - Anatomy & Physiology#The Head and Neck|head]], [[Musculoskeletal System - Anatomy & Physiology#The Head and Neck|neck]], fetlock, hock and [[Hoof - Anatomy & Physiology|hoof]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Granulomatous infection | ||
| + | **Necrosis and fistulous tracts | ||
| + | **Yellow lesions | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Branching, separated fungi | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Progressive (rather than systemic) disease | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Surgery is needed | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Rhinosporidiosis== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Rhinosporidium seeberi'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Lives in water | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Causes a chronic, benign disease | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Affects cattle, mules, horses, dogs and humans | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Causes polyps on the [[Nasal cavity - Anatomy & Physiology|nasal]] and [[Eye - Anatomy & Physiology|ocular]] mucous membranes | ||
| + | **Over 90% of cases affecting the [[Nasal cavity - Anatomy & Physiology|nasal]] mucous membranes affects male animals | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Occurs most frequently in tropical countries | ||
| + | **Also common in the USA | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Large sporangia can be seen on wet mounts | ||
| + | **Endospores visible | ||
| + | **Sporangia develop into small, globose spores | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Treatment is by surgical excision | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Sporotrichosis== | ||
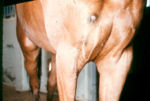
| + | [[Image:Sporotrichosis horse.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Sporotrichosis in a horse -Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath]] | ||
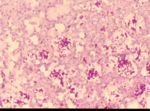
| + | [[Image:Sporotrichosis cigar cells.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Sporotrichosis cigar shaped cells -Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath]] | ||
| + | *''Sporothrix schenckii'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Occurs in soil, wood and vegetation | ||
| + | **Saprophyte of both decaying and healthy vegetation | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Worldwide | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Exogenous infections through wounds | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Sporadic infections | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Non-contageous | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Causes subcutaneous nodules or granulomas | ||
| + | **Nodules ulcerate discharging pus | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Spread via the [[Lymphatic System - Anatomy & Physiology|lymphatics]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The [[Bones and Cartilage - Anatomy & Physiology|bones]] and viscera can be involved which terminates in mortality | ||
| + | **This is rare | ||
| + | **Reported in dogs and horses | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Affects dogs, horses, cats, monkeys, mules, camels, donkeys, cattle, fowl and rodents | ||
| + | **Most commonly seen in horses as an ascending lymphocutaneous infection of the legs | ||
| + | **Can be confused with [[Subcutaneous Mycoses#Epizootic Lymphangitis|epizootic lymphangitis]] in horses | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Single cell, cigar shaped | ||
| + | **Usually found within [[Neutrophils - WikiBlood|neutrophils]] | ||
| + | **Yeast cell clusters with peripheral eosinophilic rays can be seen in tissue sections | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Stained using PAS, Gram stain (positive), fluorescent antibody and Calcofluor White | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Latex agglutination and immunodiffusion serology can be performed | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Grows on Blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar in one to three weeks | ||
| + | **At 37°C: | ||
| + | ***Colonies are smooth, cream to tan coloured and soft | ||
| + | ***No mycelium can be seen | ||
| + | **At 25°C to 27°C: | ||
| + | ***Colonies turn from white and soft to tan to brown to black | ||
| + | ***Leathery, wrinkled and coarse | ||
| + | ***Mycelium can be seen as branching septate hyphae | ||
| + | ***Conidiospores can also be seen | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Potassium iodide treatment orally | ||
| + | **[[Antifungal Drugs#Flucytosine|5-fluorocytosine]] and [[Antifungal Drugs#Polyene Antifungals|amphotericin B]] can also be used | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Further Links== | ||
| + | *Pathology of [[Mycotic skin infections - Pathology#Subcutaneous mycoses|subcutaneous mycoses]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Antifungal Drugs]] | ||
Revision as of 13:35, 29 April 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
Pythiosis
- Causes Mycotic Swamp Fever
- Also called phycomycosis
- Occurs in the USA, Australia, New Guinea, India, Brazil, Colombia, Japan, Costa Rica and Indonesia
- Pythium insidiosum
- Granulomatous infection
- Necrosis and fistulous tracts
- Yellow lesions
- Branching, separated fungi
- Progressive (rather than systemic) disease
- Surgery is needed
Rhinosporidiosis
- Rhinosporidium seeberi
- Lives in water
- Causes a chronic, benign disease
- Affects cattle, mules, horses, dogs and humans
- Causes polyps on the nasal and ocular mucous membranes
- Over 90% of cases affecting the nasal mucous membranes affects male animals
- Occurs most frequently in tropical countries
- Also common in the USA
- Large sporangia can be seen on wet mounts
- Endospores visible
- Sporangia develop into small, globose spores
- Treatment is by surgical excision
Sporotrichosis
- Sporothrix schenckii
- Occurs in soil, wood and vegetation
- Saprophyte of both decaying and healthy vegetation
- Worldwide
- Exogenous infections through wounds
- Sporadic infections
- Non-contageous
- Causes subcutaneous nodules or granulomas
- Nodules ulcerate discharging pus
- Spread via the lymphatics
- The bones and viscera can be involved which terminates in mortality
- This is rare
- Reported in dogs and horses
- Affects dogs, horses, cats, monkeys, mules, camels, donkeys, cattle, fowl and rodents
- Most commonly seen in horses as an ascending lymphocutaneous infection of the legs
- Can be confused with epizootic lymphangitis in horses
- Single cell, cigar shaped
- Usually found within neutrophils
- Yeast cell clusters with peripheral eosinophilic rays can be seen in tissue sections
- Stained using PAS, Gram stain (positive), fluorescent antibody and Calcofluor White
- Latex agglutination and immunodiffusion serology can be performed
- Grows on Blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar in one to three weeks
- At 37°C:
- Colonies are smooth, cream to tan coloured and soft
- No mycelium can be seen
- At 25°C to 27°C:
- Colonies turn from white and soft to tan to brown to black
- Leathery, wrinkled and coarse
- Mycelium can be seen as branching septate hyphae
- Conidiospores can also be seen
- At 37°C:
- Potassium iodide treatment orally
- 5-fluorocytosine and amphotericin B can also be used
Further Links
- Pathology of subcutaneous mycoses