Difference between revisions of "Type IV Hypersensitivity"
m (Text replace - 'Lymphocytes - WikiBlood' to 'Lymphocytes') |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |backcolour = FFE4E1 | ||
| + | |linkpage =Immunology - WikiBlood | ||
| + | |linktext =IMMUNOLOGY | ||
| + | |sublink1 =Hypersensitivity - WikiBlood | ||
| + | |subtext1 =HYPERSENSITIVITY | ||
| + | |pagetype =Blood | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | [[Image:Sensitisation phase Type IV Hypersensitivity.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Sensitisation phase: Type | + | [[Image:Sensitisation phase Type IV Hypersensitivity.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Sensitisation phase: Type VI hypersensitivity-Brian Catchpole RVC 2008]] |
| − | [[Image:Delayed type hypersensitivity.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Type | + | [[Image:Delayed type hypersensitivity.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Type VI hypersensitivity-Brian Catchpole RVC 2008]] |
Cell mediated hypersensitivity: | Cell mediated hypersensitivity: | ||
| − | Type IV hypersensitivity, also known as delayed hypersensitivity, involves [[Cytokines|cytokines]] being secreted from the Th-I cells, which causes the activation of [[Macrophages|macrophages]] and other T cells. | + | Type IV hypersensitivity, also known as delayed hypersensitivity, involves [[Cytokines - WikiBlood|cytokines]] being secreted from the Th-I cells, which causes the activation of [[Macrophages - WikiBlood|macrophages]] and other T cells. |
* [[Lymphocytes#Helper CD4+|'''CD4+ (helper)''']] mediated: | * [[Lymphocytes#Helper CD4+|'''CD4+ (helper)''']] mediated: | ||
| Line 14: | Line 26: | ||
** Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) kill healthy cells mistakenly thinking they are infected by a virus. | ** Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) kill healthy cells mistakenly thinking they are infected by a virus. | ||
| − | Exposure to antigen causes [[Lymphocytes#Helper CD4+|'''CD4+ T helper cells''']] to be activated leading to colonal expansion (takes 1-2 weeks). On subsequent exposure with the same antigen sensitised [[Lymphocytes#Helper CD4+|'''CD4+ T helper cells''']] secrete [[Cytokines|cytokines]] which attract and activate macrophages. The [[Macrophages|macrophages]] have an increased ability to phagocytose pathogens, which is very important for the clearance of intracellular pathogens. However if antigen exposure persists, the lytic products of the macrophages can damage healthy tissues. | + | Exposure to antigen causes [[Lymphocytes#Helper CD4+|'''CD4+ T helper cells''']] to be activated leading to colonal expansion (takes 1-2 weeks). On subsequent exposure with the same antigen sensitised [[Lymphocytes#Helper CD4+|'''CD4+ T helper cells''']] secrete [[Cytokines - WikiBlood|cytokines]] which attract and activate macrophages. The [[Macrophages - WikiBlood|macrophages]] have an increased ability to phagocytose pathogens, which is very important for the clearance of intracellular pathogens. However if antigen exposure persists, the lytic products of the macrophages can damage healthy tissues. |
==2 types:== | ==2 types:== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 37: | ||
{| style="width:60%; height:200px" border="1" align=left | {| style="width:60%; height:200px" border="1" align=left | ||
! | ! | ||
| − | ![[Atopic | + | ![[Allergic diseases - WikiClinical#1. Atopic dermatitis - Dogs and horses|'''Atopic dermatitis''']] |
!'''Contact dermatitis''' | !'''Contact dermatitis''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Pathogenesis''' | | '''Pathogenesis''' | ||
| − | | [[Type I Hypersensitivity|Type I]] | + | | [[Type I Hypersensitivity - WikiBlood|Type I]] |
| − | | [[Type IV Hypersensitivity|Type IV]] | + | | [[Type IV Hypersensitivity - WikiBlood|Type IV]] |
|- | |- | ||
| '''Time''' | | '''Time''' | ||
| Line 49: | Line 61: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Pathology''' | |'''Pathology''' | ||
| − | | [[Mast Cells|mast cells]], [[Eosinophils|eosinophils]] | + | | [[Mast Cells - WikiBlood|mast cells]], [[Eosinophils - WikiBlood|eosinophils]] |
| − | | [[Monocytes|mononuclear cells]] | + | | [[Monocytes - WikiBlood|mononuclear cells]] |
|} | |} | ||
<Br clear="left"> | <Br clear="left"> | ||
===2. Granulomatous=== | ===2. Granulomatous=== | ||
| − | * Intense activation of T cells, [[Cytokines|cytokine]] release and [[Macrophages|macrophage]] activation cause necrosis of surrounding tissue, granuloma formation leading to destruction of host tissue. | + | * Intense activation of T cells, [[Cytokines - WikiBlood|cytokine]] release and [[Macrophages - WikiBlood|macrophage]] activation cause necrosis of surrounding tissue, granuloma formation leading to destruction of host tissue. |
| − | * Composed of epithelial cell, [[Macrophages#Giant cells|giant cells]] and [[Macrophages|macrophage]] in response to infection, for example: | + | * Composed of epithelial cell, [[Macrophages - WikiBlood#Giant cells|giant cells]] and [[Macrophages - WikiBlood|macrophage]] in response to infection, for example: |
** [[:Category:Mycobacterium species|''Mycobacterium tubercle'']] | ** [[:Category:Mycobacterium species|''Mycobacterium tubercle'']] | ||
** Schistosome eggs | ** Schistosome eggs | ||
| Line 65: | Line 77: | ||
===Tuberculin test=== | ===Tuberculin test=== | ||
* Injection of intradermal antigen into the skin. | * Injection of intradermal antigen into the skin. | ||
| − | * A skin reaction (infiltration of lymphocytes and [[Monocytes]]) peaking at 48-72 hours indicates prior exposure to the antigen or ongoing infection. | + | * A skin reaction (infiltration of lymphocytes and [[Monocytes - WikiBlood]]) peaking at 48-72 hours indicates prior exposure to the antigen or ongoing infection. |
* It is used for TB testing cattle; the antigen is purified protein derivative-PPD from [[:Category:Mycobacterium species|''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'']]. | * It is used for TB testing cattle; the antigen is purified protein derivative-PPD from [[:Category:Mycobacterium species|''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'']]. | ||
* Presently in the UK the animal is culled if it has a positive skin reaction. | * Presently in the UK the animal is culled if it has a positive skin reaction. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 12:38, 12 June 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
Introduction
Cell mediated hypersensitivity:
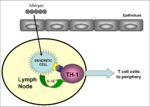
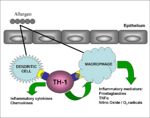
Type IV hypersensitivity, also known as delayed hypersensitivity, involves cytokines being secreted from the Th-I cells, which causes the activation of macrophages and other T cells.
- CD4+ (helper) mediated:
- Abnormal activation of macrophages in healthy tissues.
- Macrophage production of inflammatory mediators and MMP (matrix metalloproteinase) enzymes cause tissue damage.
- CD8+ (cytotoxic) mediated:
- Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) kill healthy cells mistakenly thinking they are infected by a virus.
Exposure to antigen causes CD4+ T helper cells to be activated leading to colonal expansion (takes 1-2 weeks). On subsequent exposure with the same antigen sensitised CD4+ T helper cells secrete cytokines which attract and activate macrophages. The macrophages have an increased ability to phagocytose pathogens, which is very important for the clearance of intracellular pathogens. However if antigen exposure persists, the lytic products of the macrophages can damage healthy tissues.
2 types:
1. Contact
- Involves simple chemicals (antigens) which bind to skin proteins:
- Nickle
- Rubber
- Poison ivy
Distinguishing contact from immediate hypersensitivity
| Atopic dermatitis | Contact dermatitis | |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogenesis | Type I | Type IV |
| Time | 20 mins | 24-48 hours |
| Distribution | face, nose, eyes, feet, perineum | hairless regions |
| Antigens | foods, pollens, fleas, inhaled allergens | chemicals, dyes |
| Diagnosis | "prick" test | patch test for delayed hypersensitivity |
| Pathology | mast cells, eosinophils | mononuclear cells |
2. Granulomatous
- Intense activation of T cells, cytokine release and macrophage activation cause necrosis of surrounding tissue, granuloma formation leading to destruction of host tissue.
- Composed of epithelial cell, giant cells and macrophage in response to infection, for example:
- Mycobacterium tubercle
- Schistosome eggs
- Granulomas can obstruct normal organ function:
- Lungs: fills up with cells leading to impaired function
- Brain/liver: very severe
Tuberculin test
- Injection of intradermal antigen into the skin.
- A skin reaction (infiltration of lymphocytes and Monocytes - WikiBlood) peaking at 48-72 hours indicates prior exposure to the antigen or ongoing infection.
- It is used for TB testing cattle; the antigen is purified protein derivative-PPD from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Presently in the UK the animal is culled if it has a positive skin reaction.