Difference between revisions of "Fasciola hepatica"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{review}} | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Taxobox | ||
| + | |name =''Fasciola hepatica | ||
| + | |kingdom =Animalia | ||
| + | |phylum =Platyhelminthes | ||
| + | |class =[[:Category:Trematodes|Trematoda]] | ||
| + | |sub-class =Digenea | ||
| + | |order =Echinostomida | ||
| + | |super-family = | ||
| + | |family =Fasciolidae | ||
| + | |sub-family = | ||
| + | |genus =Fasciola | ||
| + | |species =Fasciola hepatica | ||
| + | }} | ||
{| cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0" border="1" | {| cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
| Line 14: | Line 28: | ||
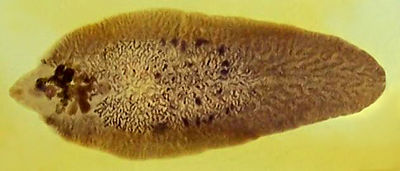
[[Image:Fasciola hepatica.jpg|400px|thumb|right|''Fasciola hepatica'' <br> Adam Cuerden 2007, Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Fasciola hepatica.jpg|400px|thumb|right|''Fasciola hepatica'' <br> Adam Cuerden 2007, Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Life Cycle== | ==Life Cycle== | ||
Revision as of 13:04, 28 July 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
| Fasciola hepatica | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Platyhelminthes |
| Class | Trematoda |
| Sub-class | Digenea |
| Order | Echinostomida |
| Family | Fasciolidae |
| Genus | Fasciola |
| Species | Fasciola hepatica |
| Also known as: | Liver Fluke |
Introduction
Fasciola Hepatica is an hepatic parasite found mainly in ruminants, namely cows, sheep and goats, but also known to affect horses, pigs, deer and man. It is found Worldwide, and within the UK, with its prevalence ever increasing. It is responsible for a 10-15% production loss in each infected animal, as it affects meat, milk and wool production, so is of huge economic consequence.
Fasciola Hepatica has a definitive ruminant mammalian host and an intermediate molluscan host (indirect life cycle). Within Europe the intermediate host is almost exclusively the amphibious snail Lymnaea truncatulata. The snail habitat is crucial to the survival of the parasite, so wet conditions are favourable to the development and spread of Fasciola hepatica.
Life Cycle
Adult flukes in the bile ducts shed eggs directly into the bile, which then subsequently enter the intestine. Eggs are then passed out in the faeces of the mammalian host, where they develop and hatch releasing motile ciliated miracidia. These require 9-10 days at optimal temperatures, of around 22-26 degrees. The miracidium have a short life and must locate a suitable snail, the intermediate host, within approximately 3 hours if they are to be effective and continue the life cycle.
If successful, the miracidium will then develop into sporocysts, then enter the redial stages to the final stages within the intermediate host, which is development into cercaria. These cercaria are then released from the snail, and attach to surfaces such as the tips of grass. Here they encyst and form metacercaria. This represents the infective stage of the lifecycle.
Development from miracidium into metacercariae takes around 6-7 weeks under favourable conditions, however, this period can be much longer in unfavourable conditions.
The final host, or the definitive host then ingests the metacercariae from the grass on the pasture, and these pass through the body into the intestine, where they excyst in the wall of the small intestine. They then travel through the wall of the gut, and migrate into the liver, through the liver parenchyma. The young liver flukes migrate through the liver for around 6-8 weeks before entering the bile ducts. They may also migrate into the gall bladder, where they reach full sexual maturity.
The prepatent period of Fasciola hepatica is 10-12 weeks. In untreated sheep it may survive and continue to infect for many years. In cattle it is usually less than 1 year.
Identification
The egg is relatively large; around 140μm x 70μm. It is oval shaped, with a thin outer shell, and is browny-yellow.
The fully mature adult fluke is a dark brown colour, and around 3cm in length.
Snail biology
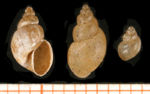
Lymnaea truncatula
Lympnea truncatula is around 5-10mm long. It has a distinctive brown-black shell, with 5-6 spirals present on the outer surface. The first spiral is approximately half the total length of the snail.
It feeds on green slime, and when this is present in abundance, they may multiply rapidly.
Most die in the British winter, due to the harsh, cold conditions, but they may survive in milder winters. Survivors will lay eggs in spring, which will hatch in June.
Habitats
Lymnaea are found predominantly in muddy areas, but do not survive well in highly acidic soils. Habitats may be permanent; seen in dry summers or temporary; found in wet summers.
Epidemiology
In temperate areas, there are two superimposed epidemiological cycles, known as the summer and winter infections of the snail. On mainland Britain, the summer cycle predominates as a high proportion of snails perish during the winter, but very occasionally, weather sequences allow the winter cycle to affect the pattern of disease. On the west coast of Ireland, the winter cycle of events determines the timing of clinical outbreaks.
Summer infection of the snail
The fluke eggs passed in spring will hatch in June. This coincides with the hatching of the snail. The miracidia will then infect the newly hatched snails, mature and then multiply within the snail hepatopancreas during the summer months.
The cercariae are shed from late August onwards. The metacercariae develop and are ingested by a host; the sheep for example. The immature flukes then migrate through the liver, causing acute disease between the months of September and November, or chronic disease from January onwards.
Winter infection of the snail
In this case the fluke eggs are passed in the late summmer, which then infect the snails. Environmental conditions play a vital role in the success of the fluke development. Temperatures below 10 degrees will see the development being haltered, and the flukes will remain trapped in the hibernating snails throughout the winter. Development will then resume when temperatures rise above 10 degrees. The cercariae are then shed from July, and disease may be seen from August onwards.
Pathogenesis
The severity of the infection is mainly dependent on the number of metacercariae ingested. The Pathogenesis is often described as two-fold. The first stage occurring when the parasite migrates through the liver parenchyma, causing liver damage and haemorrhage. The second phase occurs when the parasite is in the bile ducts, and damage is a result of the haematophagic activity of the adult flukes.
References
Taylor, M.A, Coop, R.L., Wall,R.L. (2007) Veterinary Parasitology Blackwell Publishing
G.L. Pritchard et al., Emergence of fasciolosis in cattle in East Anglia, The Veterinary Record, November 5, 2005.