Difference between revisions of "Yeast-like Fungi - Flashcards"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (3 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |linkpage =Yeast-like fungi | ||
| + | |linktext =YEAST-LIKE FUNGI | ||
| + | |sublink1 =Flash Cards - WikiBugs | ||
| + | |subtext1 =WIKIBUGS FLASHCARDS | ||
| + | |pagetype =Bugs | ||
| + | }} | ||
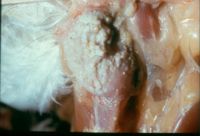
[[Image:Sour Crop.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Sour Crop - Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath]] | [[Image:Sour Crop.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Sour Crop - Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath]] | ||
===Candidosis=== | ===Candidosis=== | ||
| Line 87: | Line 94: | ||
*Ear canal | *Ear canal | ||
*Skin | *Skin | ||
| − | |l1=Yeast-like fungi#Malassezia | + | |l1=Yeast-like fungi#Malassezia pachydermidis |
| − | |q2=What is the pathogenesis of ''Malassezia | + | |q2=What is the pathogenesis of ''Malassezia pachydermidis'' infections? |
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| − | * | + | *Regional lesions on the muzzle, ears, interdigital area and the perianal region |
| − | Regional lesions on the muzzle, ears, interdigital area and the perianal region | ||
*Infection can also be generalised | *Infection can also be generalised | ||
*Erythematous, hyperpigmented, lichenified and scaly lesions with alopecia | *Erythematous, hyperpigmented, lichenified and scaly lesions with alopecia | ||
|l2=Yeast-like fungi#Malassezia pachydermidis | |l2=Yeast-like fungi#Malassezia pachydermidis | ||
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
| − | |||
===Rhodotorula=== | ===Rhodotorula=== | ||
<FlashCard questions="1"> | <FlashCard questions="1"> | ||
| Line 129: | Line 134: | ||
|l2=Trichosporonosis | |l2=Trichosporonosis | ||
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 14:56, 19 August 2010
|
|
Candidosis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What are the three important species of Candida in animal infections? |
|
Link to Article | |
| What are the clinical signs of a sour crop infection? |
|
Link to Article | |
| What other conditions are Candida spp. implicated in? |
|
Link to Article | |
| How would you demonstrate a Candida infection? |
|
Link to Article | |
Cryptococcosis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is the main pathogenic species of Cryptococcus? | C. neoformans
|
Link to Article | |
| Where is Cryptococcus found in the environment? |
|
Link to Article | |
| Which body systems are affected? |
|
Link to Article | |
| Where is the most common site of infection in cats? | The tip of the nose
|
Link to Article | |
| How would you demonstrate a cryptococcosis infection? |
|
Link to Article | |
Geotrichosis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| Which organs are usually affected in geotrichosis infections? |
|
Link to Article | |
| True or False: Geotrichosis infections are usually diagnosed post-mortem | True
|
Link to Article | |
Malassezia pachydermidis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| Where in the body is Malassezia pachydermidis usually found? |
|
Link to Article | |
| What is the pathogenesis of Malassezia pachydermidis infections? |
|
Link to Article | |
Rhodotorula
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What infections of dogs and horses are Rhodotorula spp. involved in? |
|
Link to Article | |
Torulopsis glabrata
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What infections are Torulopsis spp. involved in? |
|
Link to Article | |
Trichosporonosis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What infection is T. capitum involved in? | Bovine mastitis
|
Link to Article | |
| What infections are Trichosporonosis beigelii involved in? |
|
Link to Article | |