Difference between revisions of "Otodectes cynotis"
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{review}} |
| + | |||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
|name =''Otodectes cynotis'' | |name =''Otodectes cynotis'' | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ''Otodectes cynotis'' mites are [[Non-Burrowing Mites|surface mites]]. They are the cause of [[Otodectic Dermatosis|otodectic skin infestation]], the most common mange of dogs and cats in the world. They are also found in the fox and the ferret. The mites inhabit the inner ear and feed on ear debris, they appear white in colour. | |
| − | + | ==Identification== | |
| − | |||
The mites have closed keratinous bars, '''apodemes''' on their ventral surface. They are smaller in size than [[psoroptes cuniculi]] and have short pedicles on their first and second pairs of legs. | The mites have closed keratinous bars, '''apodemes''' on their ventral surface. They are smaller in size than [[psoroptes cuniculi]] and have short pedicles on their first and second pairs of legs. | ||
==Lifecycle== | ==Lifecycle== | ||
| + | |||
The Life cycle of an ''Otodectes'' mite takes '''3 weeks'''. The females lay around five eggs a day on the surface of the ear canal. Four days later, larvae hatch and become nymphs. There are two nymphal stages before an adult mite is formed. | The Life cycle of an ''Otodectes'' mite takes '''3 weeks'''. The females lay around five eggs a day on the surface of the ear canal. Four days later, larvae hatch and become nymphs. There are two nymphal stages before an adult mite is formed. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Pathogenesis== |
| − | |||
| − | + | The majority of cats harbour the mites, however only a few show symptoms. Transmission of the mites occurs whilst kittens are suckling. | |
| + | The mites are a common cause of [[Otitis Externa - Small Animal|otitis externa]] in dogs, which leads to the production of a brown waxy exudate. Secondary infection can also occur. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Test yourself with the Mites Flashcards== |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Mites_Flashcards|Mites Flashcards]] | |
| − | == | + | ==Literature Search== |
| − | + | [[File:CABI logo.jpg|left|90px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | '' | + | Use these links to find recent scientific publications via CAB Abstracts (log in required unless accessing from a subscribing organisation). |
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?rowId=1&options1=AND&q1=%22Otodectes+cynotis%22&occuring1=title&rowId=2&options2=AND&q2=&occuring2=freetext&rowId=3&options3=AND&q3=&occuring3=freetext&x=67&y=17&publishedstart=yyyy&publishedend=yyyy&calendarInput=yyyy-mm-dd&la=any&it=any&show=all ''Otodectes cynotis'' publications] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | [[Category:Non-Burrowing_Mites]] | ||
| − | + | [[Category:To_Do_-_AimeeHicks]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | ||
[[Category:Expert_Review]] | [[Category:Expert_Review]] | ||
Revision as of 12:11, 4 October 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
| Otodectes cynotis | |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Arthropoda |
| Class | Arachnida |
| Order | Astigmata |
| Family | Psoroptidia |
| Genus | Otodectes |
| Species | O.cynotis |
Also known as: Ear mite
Introduction
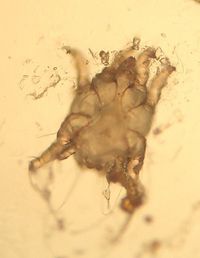
Otodectes cynotis mites are surface mites. They are the cause of otodectic skin infestation, the most common mange of dogs and cats in the world. They are also found in the fox and the ferret. The mites inhabit the inner ear and feed on ear debris, they appear white in colour.
Identification
The mites have closed keratinous bars, apodemes on their ventral surface. They are smaller in size than psoroptes cuniculi and have short pedicles on their first and second pairs of legs.
Lifecycle
The Life cycle of an Otodectes mite takes 3 weeks. The females lay around five eggs a day on the surface of the ear canal. Four days later, larvae hatch and become nymphs. There are two nymphal stages before an adult mite is formed.
Pathogenesis
The majority of cats harbour the mites, however only a few show symptoms. Transmission of the mites occurs whilst kittens are suckling. The mites are a common cause of otitis externa in dogs, which leads to the production of a brown waxy exudate. Secondary infection can also occur.
Test yourself with the Mites Flashcards
Literature Search
Use these links to find recent scientific publications via CAB Abstracts (log in required unless accessing from a subscribing organisation).
Otodectes cynotis publications