Difference between revisions of "Sarcoptic Mange"
TestStudent (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | == | + | Also known as: '''''Scabies''''' |
| − | [[Image:Puppy sarcoptic mange.jpg|thumb|right|150px| | + | |
| − | + | == Introduction == | |
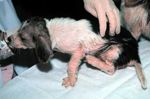
| + | [[Image:Puppy sarcoptic mange.jpg|thumb|right|150px|<b>Puppy with sarcoptic mange</b> <br /> Caroldermoid 2006, Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
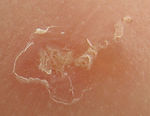
| + | [[Image:Scabies human skin pruritus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Scabies on human skin resulting in pruritus - Geary 2006,Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | Sarcoptic mange is a relatively common skin disease of dogs and other species, in the UK. It can affect animals of all ages, but may be most severe in puppies. It can also transfer to humans where it cannot burrow, but will cause a pruritic, erythrematous dermatitis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Transmission of the disease is by direct contact. | ||
| − | + | The mite ''[[Sarcoptes|Sarcoptes scabiei]]'' is the cause. Strains of ''S. scabiei'' can be passed between different animals and cause clinical signs although the infection is likely to resolve spontaneously and be unlikely to establish. | |
| − | + | The disease is common in the dog, rare in the cat and quite common in pigs, where the disease is also severe. In cattle, sheep and horses the disease is notifiable and rare. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Sarcoptic Mange is an important condition in pigs where 35% of pigs are asymptomatic carriers of the infection. Transmission is usually via direct contact from sow to piglets whilst suckling and from boars to gilts at service. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Clinical Signs == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The disease is characterised by erythema with papule formation, scale and crust formation, alopecia and intense pruritus for at least one week. This will often appear clinically as self-inflicted trauma wounds and scab formation. | |
| − | + | There will be a wrinkling and thickening of skin in the chronic cases too and [[Hypersensitivity - Introduction|hypersensitivity]] may develop. | |
| − | |||
| + | In the dog, clinical signs are characteristic with the first signs appearing at edges of ears, then progresses to muzzle, face and elbows. It is intensely pruritic. | ||
| − | + | First signs of infestation in pigs appear on the ears before spreading to the rest of the body, which is the same as dogs. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Diagnosis == | |
| − | + | Diagnosis can be made by the characteristic clinical signs. A deep skin scraping should be taken (skin scraping until capillary blood appears) then viewed under the microscope for identification of mites. Slides are prepared by placing material on a slide, adding 10% KOH and warming over a bunsen flame. Adults, eggs, immature mites and faecal pellets can be seen microscopically. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | A '''serological test''' to determine the presence of anti-''Sarcoptes'' [[IgG]] is also available in dogs. This test is reported to have a sensitivity ranging between 83% and 92% and a specificity ranging between 89.5% and 92%. | |
| − | + | == Treatment and Control== | |
| − | + | An [[Ectoparasiticides|acaricide]] should be used to treat this infection. | |
| − | + | Both infected and in-contact animals should be treated, older products have to be given in repeat treatments. Avermectins are effective in farm animals and Selamectin is available as a good spot-on for dogs. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | All bedding and materials that have come into contact with the animal, e.g. the car, must be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected. | |
| − | + | Control for pigs includes treating sows before entering the farrowing pen and treating boars at 6 month intervals. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Also see: <big><b>[[Mites - Ferrets#Scabies|Scabies in Ferrets]]</b></big> | |
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/Content/Disease/dis02359.asp Sarcoptic mange] | ||
| − | = | + | |flashcards = [[Mites Flashcards|Mites Flashcards]] |
| − | + | [[Small Animal Dermatology Q&A 11]] | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | |||
| − | === | + | == References == |
| − | |||
| − | + | Foster, A, and Foll, C. (2003) '''BSAVA small animal dermatology '''(second edition) ''British Small Animal Veterinary Association'' | |
| − | + | Fox, M and Jacobs, D. (2007) '''Parasitology Study Guide Part 1: Ectoparasites''''' Royal Veterinary College '' | |
| − | + | Patel, A. (2008) '''Small animal dermatology''' ''Elsevier Health Sciences'' | |
| − | + | Taylor, D.J. (2006) '''Pig Diseases '''(Eighth edition)'' St Edmunsdbury Press ltd'' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{review}} | |
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Expert_Review - Farm Animal]] [[Category:Expert Review - Small Animal]][[Category:Dermatological_Diseases_-_Dog]] [[Category:Dermatological_Diseases_-_Cat]] [[Category:Dermatological_Diseases_-_Cattle]] [[Category:Dermatological_Diseases_-_Pig]] [[Category:Dermatological_Diseases_-_Sheep]] [[Category:Dermatological_Diseases_-_Horse]] [[Category:Integumentary_System_-_Mite_Infections]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Zoonoses]] |
| − | [[Category: | ||
Latest revision as of 12:16, 23 August 2015
Also known as: Scabies
Introduction
Sarcoptic mange is a relatively common skin disease of dogs and other species, in the UK. It can affect animals of all ages, but may be most severe in puppies. It can also transfer to humans where it cannot burrow, but will cause a pruritic, erythrematous dermatitis.
Transmission of the disease is by direct contact.
The mite Sarcoptes scabiei is the cause. Strains of S. scabiei can be passed between different animals and cause clinical signs although the infection is likely to resolve spontaneously and be unlikely to establish.
The disease is common in the dog, rare in the cat and quite common in pigs, where the disease is also severe. In cattle, sheep and horses the disease is notifiable and rare.
Sarcoptic Mange is an important condition in pigs where 35% of pigs are asymptomatic carriers of the infection. Transmission is usually via direct contact from sow to piglets whilst suckling and from boars to gilts at service.
Clinical Signs
The disease is characterised by erythema with papule formation, scale and crust formation, alopecia and intense pruritus for at least one week. This will often appear clinically as self-inflicted trauma wounds and scab formation.
There will be a wrinkling and thickening of skin in the chronic cases too and hypersensitivity may develop.
In the dog, clinical signs are characteristic with the first signs appearing at edges of ears, then progresses to muzzle, face and elbows. It is intensely pruritic.
First signs of infestation in pigs appear on the ears before spreading to the rest of the body, which is the same as dogs.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis can be made by the characteristic clinical signs. A deep skin scraping should be taken (skin scraping until capillary blood appears) then viewed under the microscope for identification of mites. Slides are prepared by placing material on a slide, adding 10% KOH and warming over a bunsen flame. Adults, eggs, immature mites and faecal pellets can be seen microscopically.
A serological test to determine the presence of anti-Sarcoptes IgG is also available in dogs. This test is reported to have a sensitivity ranging between 83% and 92% and a specificity ranging between 89.5% and 92%.
Treatment and Control
An acaricide should be used to treat this infection.
Both infected and in-contact animals should be treated, older products have to be given in repeat treatments. Avermectins are effective in farm animals and Selamectin is available as a good spot-on for dogs.
All bedding and materials that have come into contact with the animal, e.g. the car, must be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected.
Control for pigs includes treating sows before entering the farrowing pen and treating boars at 6 month intervals.
Also see: Scabies in Ferrets
| Sarcoptic Mange Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Mites Flashcards |
References
Foster, A, and Foll, C. (2003) BSAVA small animal dermatology (second edition) British Small Animal Veterinary Association
Fox, M and Jacobs, D. (2007) Parasitology Study Guide Part 1: Ectoparasites Royal Veterinary College
Patel, A. (2008) Small animal dermatology Elsevier Health Sciences
Taylor, D.J. (2006) Pig Diseases (Eighth edition) St Edmunsdbury Press ltd
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt695cb23e3b42a8_47596659 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt695cb23e4158a7_42803965 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt695cb23e47d607_45184439
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |